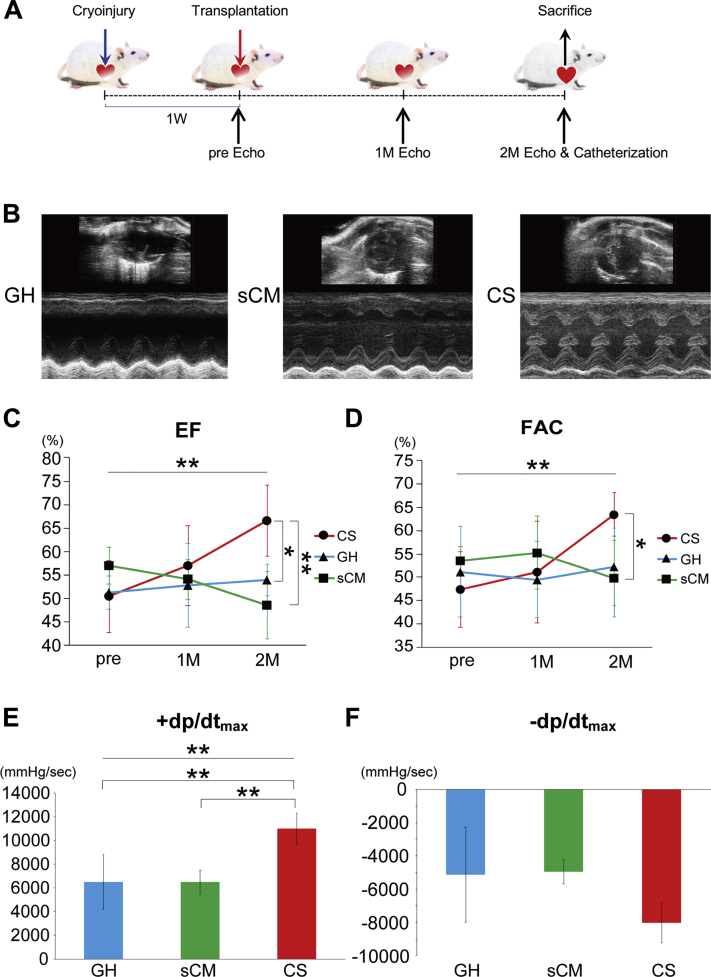
Figure 2.
hiPSC-Derived CSs Significantly Improved Cardiac Function in Immunocompromised Rats With Heart Failure
(A) Transplantation protocol for immunocompromised rats is shown. (B) Representative short-axis and M-mode images of hearts in the control (gelatin hydrogel [GH]), single CM (sCM), and CS groups. (C) Cardiac ejection fraction (EF) significantly improved in the CS group (p < 0.001). Post hoc analysis also showed the significant improvement in the CS group at 2 months (CS vs. GH; p = 0.022 CS vs. sCM; p = 0.002). (D) Cardiac fractional area change (FAC) significantly improved in the CS group (p = 0.005). Post hoc analysis showed that the CS group significantly improved at 2 months in comparison with the sCM group, and tended to improve in comparison with the GH group (CS vs. GH: p = 0.073; CS vs. sCM: p = 0.029). (E) Hemodynamic data showed that the +dp/dtmax significantly improved in the CS group (p = 0.003). Post hoc analysis showed that the CS group significantly improved +dp/dtmax at 2 months (CS vs. GH: p = 0.003; CS vs. sCM: p = 0.009). (F) Diastolic function (–dp/dtmax) tended to improve in the CS group (p = 0.129). ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01. M = month; W = week.