Figure 15.
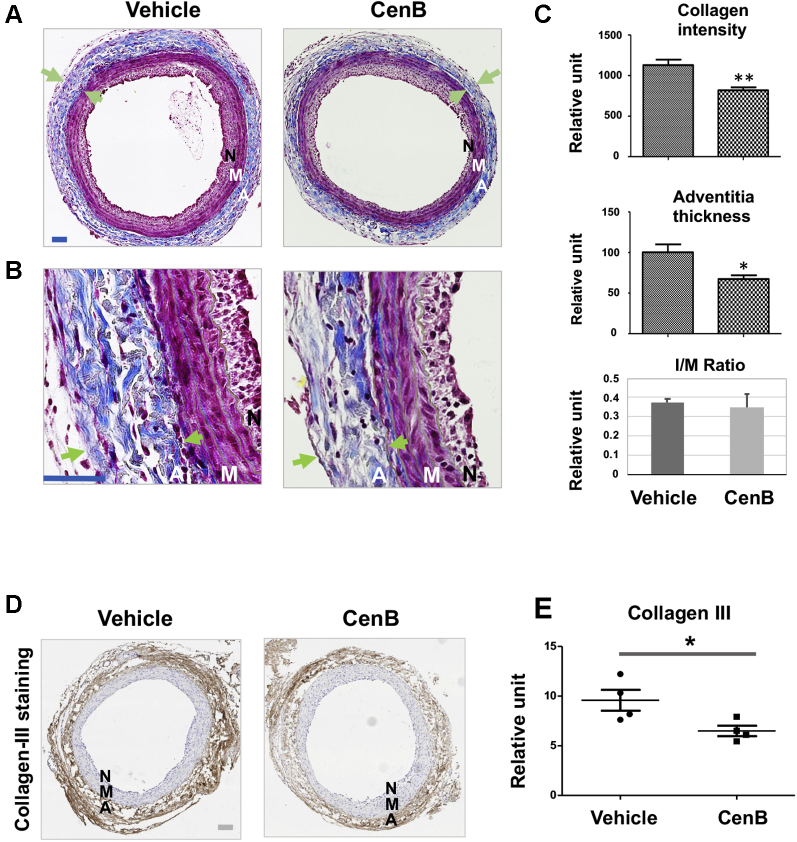
Perivascular Administration of PLK4 Inhibitor Reduces Collagen Content and Thickness of the Adventitia in the Model of Rat Carotid Artery Injury
After balloon angioplasty of the rat common carotid artery, vehicle or PLK4 inhibitor (CenB, 100 μg per rat) dissolved in a hydrogel mix was applied around the adventitia of the injured artery. Arteries were harvested at day 7 after injury; cross-sections were used for Masson’s trichrome staining for collagen. (A) Representative sections from the arteries treated with vehicle (equal amount of DMSO) or CenB. Collagen is stained blue; the adventitia thickness is indicated by 2 arrows. The anatomy of the artery wall is labeled as A (adventitia), M (media), and N (neointima). Scale bar: 100 μm. (B) Magnified areas of the images in A. (C) Quantification. Collagen content (staining intensity) and thickness of the adventitia were normalized to the overall vessel size measured as the length of the external elastic lamina (the border between blue and red layers). Neointimal hyperplasia was measured as the intima/media area ratio (I/M). Mean ± SEM, n = 5 animals per group. Student t-test: ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01. (D) Representative immunohistologic images for collagen III. Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) Quantification. The staining intensity (measured with the use of ImageJ above a threshold) was normalized to the perimeter of the external elastic lamina. The data from different sections were pooled to generate the mean for each animal. The means from all animals in each group were then averaged, and the final mean ± SEM was calculated. Student t-test: ∗p < 0.05; n = 4 animals per group indicated by the 4 data points in the plot. Abbreviations as in Figure 1.