Figure 1:
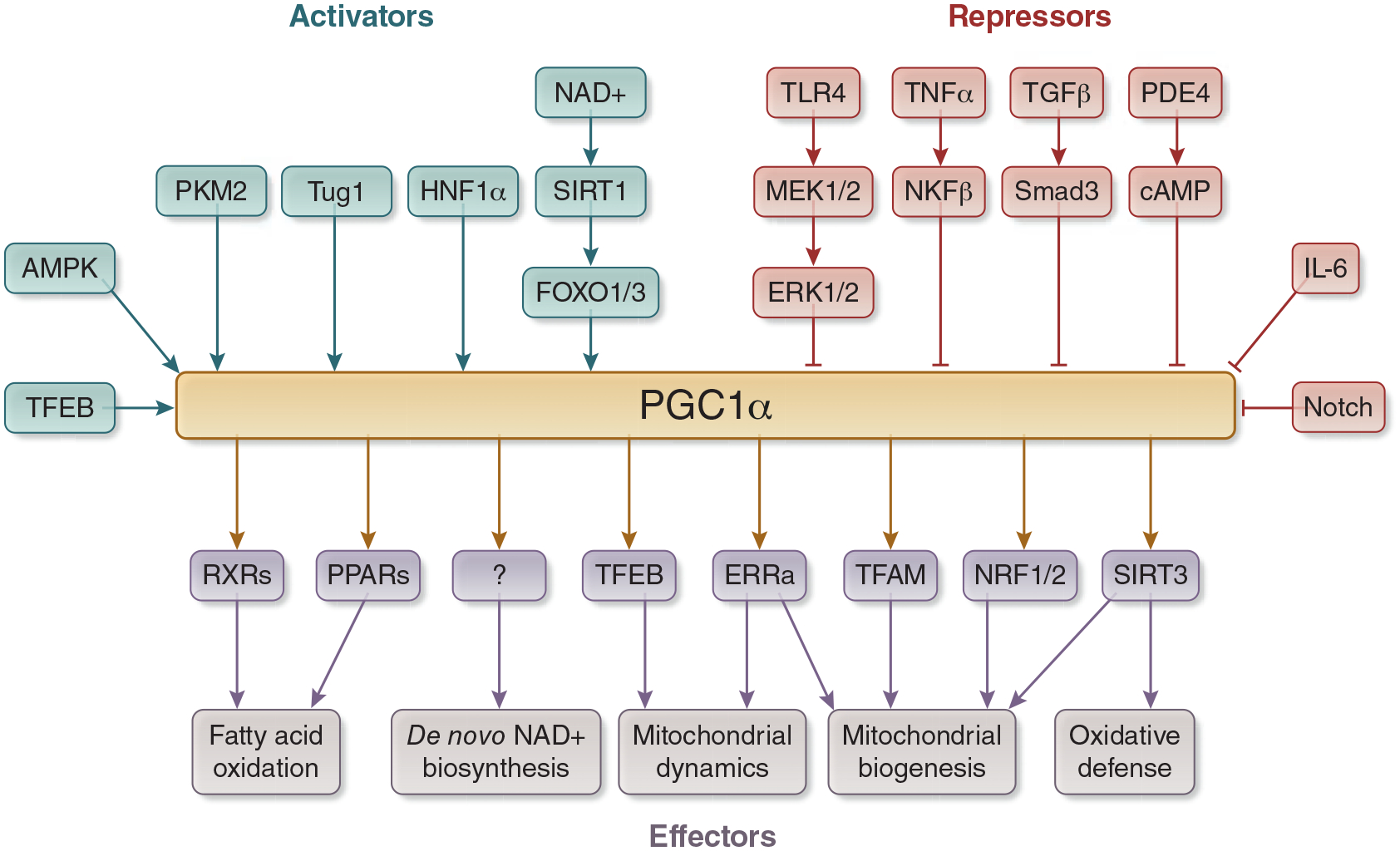
Regulators and Effectors of PGC1α. PGC1α is activated by many transcription factors, including SIRT1, AMPK, TFEB, PKM2, Tug1, and HNF1α. Transcription factors typically involved in inflammatory and pro-fibrotic pathways repress PGC1α, including TLR4, TNFα, TGFβ, PDE4, IL-6. PGC1α activates fatty acid oxidation through PPARs and RXRs. It enhances de novo biosynthesis of NAD+ through mechanisms that have yet to be delineated, and it controls mitochondrial health through activation of ERRα, TFAM, NRF1/2, and SIRT3. Abbreviations: PGC1α - Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha, SIRT - sirtuin, AMPK - 5’ AMP-activated protein kinase, TFEB - transcription factor EB, PKM2 - pyruvate kinase M2, Tug1 - Taurine Up-Regulated 1, HNF1α - hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha, TLR4 - toll-like receptor 4, TNFα - tumor necrosis factor alpha, TGFβ - transforming growth factor beta, PDE4 - phosphodiesterase 4, IL-6 - interleukin 6, PPARs - Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, RXRs - retinoid X receptors, ERRα - estrogen-related receptor alpha, TFAM - transcription factor A, mitochondrial, NRF - nuclear respiratory factor.
