Figure 3:
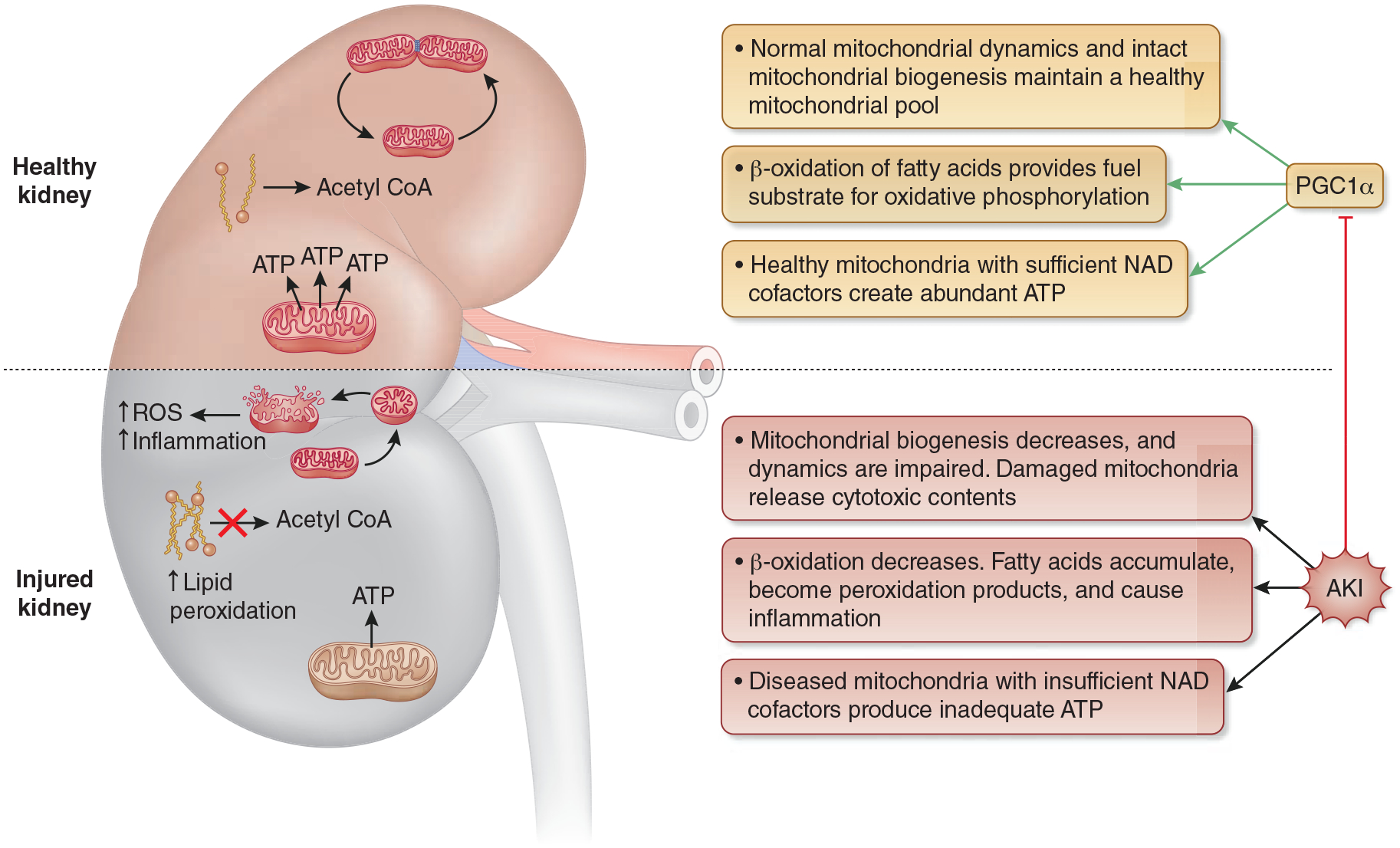
The Role of PGC1α in AKI. With AKI-induced suppression of PGC1α, mitochondrial biogenesis decreases, and mitochondrial dynamics are altered. The result is an insufficient quantity and lower quality pool of mitochondria. When mitochondrial injury is too significant to be safely disposed through normal mitochondrial dynamics, injured mitochondria undergo fragmentation and release damaging contents into the cells, which leads to increased ROS production and inflammation. The decreased availability of healthy mitochondria combined with reduced expression of ETC complexes, leads to decreased ATP production and cellular energy deprivation. Finally, PGC1α suppression leads to reduced fatty acid flux through β-oxidation with a resultant fatty acid build up that can also be damaging to cellular health. Abbreviations: PGC1α - Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha, ROS - reactive oxygen species, ETC - electron transport chain, ATP - adenosine triphosphate, NAD - nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
