Figure 2: CDDO-Im regulates IL-17A and IL-22 responses in Th17 cells:
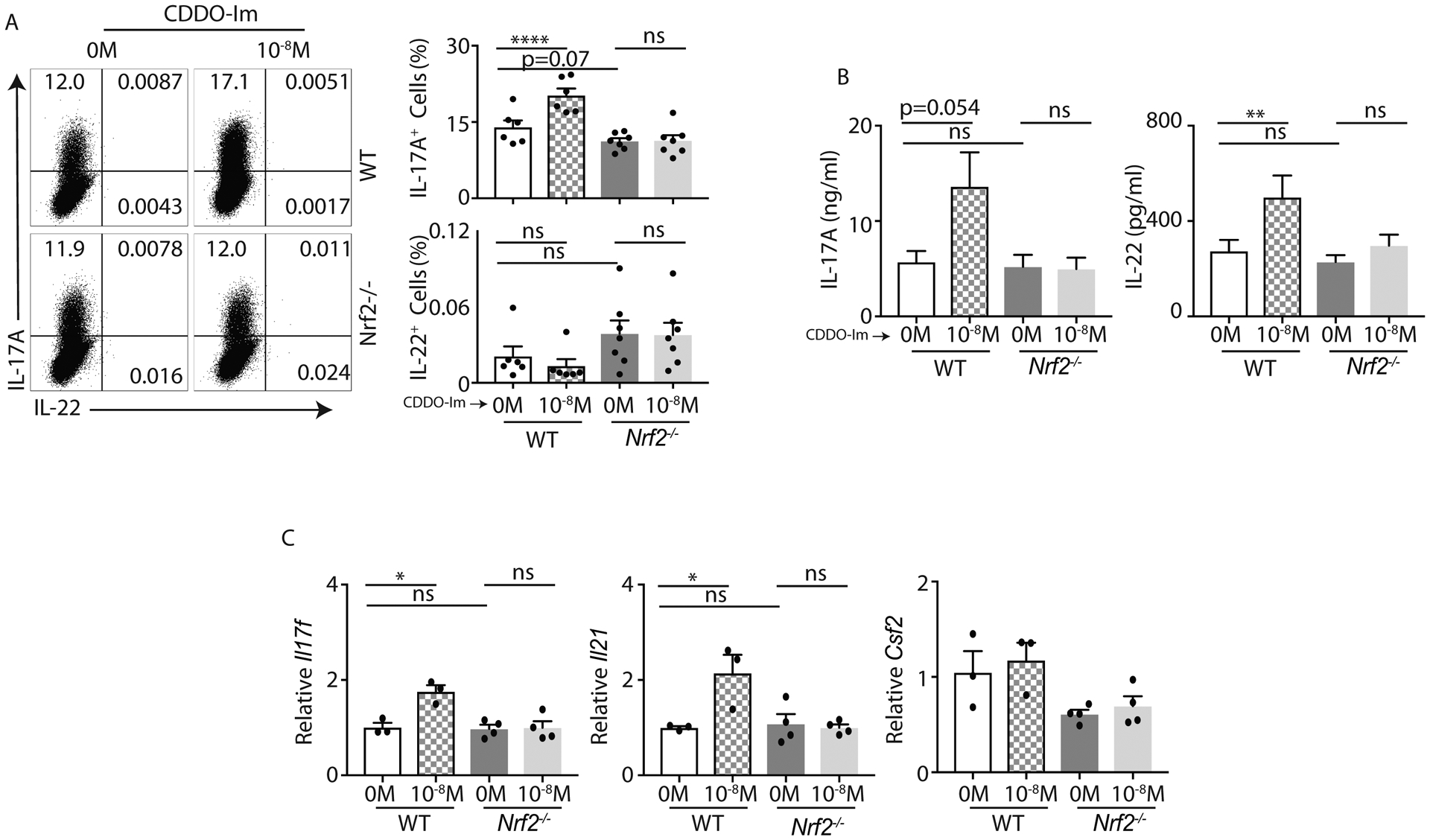
A and B) Naïve CD4+ T cells from C57BL/6 (WT) and Nrf2−/− mice were polarized to Th17 cells in presence of CDDO-Im or vehicle control. After 4-day culture, cells were restimulated with BD leukocyte activation cocktail for 4 hours and stained with anti-CD45, anti-CD3, anti-CD4, anti-IL-17A and anti-IL-22 antibodies. CD4+ T cells (gated on CD45+CD3+CD4+) producing IL-17A or IL-22 were analyzed by flow cytometry. Data show representative image (left panel) and percentage (right panel) of CD4+ T cells producing IL-17A and IL-22 in response to CDDO-Im or control vehicle (DMSO) stimulation. The concentration of IL-17A and IL-22 in the culture medium on day 4 was quantified by ELISA (B).
C) qPCR data show Il17f, Il21 and Csf2 expression on CDDO-Im or vehicle stimulated Th17 cells from WT and Nrf2−/− mice at 96 hours post stimulation.
Figure 2A and 2B were generated from 2 independent experiments. Each symbol indicates experiments from a separate animal. Data presented as mean ± SEM on relevant graphs. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ****P ≤ 0.0001 (One-Way ANOVA).
