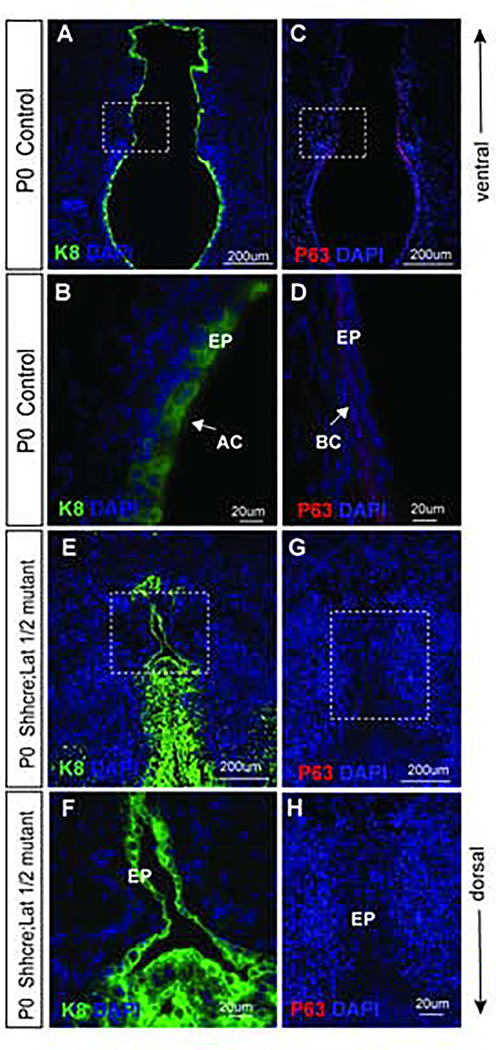
Figure 8: Inactivation of Lats1 and Lats2 results in the incomplete separation of the VF epithelium.
(A, B, and E, F) Immunofluorescence analysis of VF epithelial marker K8 (green) at P0 in transverse sections of the VF in controls (A, B) and Shhcre;Lats mutants (E,F). Bracketed regions in the panels of A and E are magnified in the B, F at 60X magnification respectively. Strong K8 (green) staining is seen in the VF epithelial layer in control and mutant VF epithelial cells. In Shhcre;Lats mutants K8 (green) staining of multilayered progenitors is seen in the not entirely separated VF epithelium. A white solid arrow in the panel of B denotes K8 positive VF apical cell layers. (C,D and G,H) Immunofluorescence analysis of p63 (red) staining in transverse sections of control (C, D) and Shhcre;Lats mutant VF (G, H). Bracketed regions in the panels of C and G are magnified in the panels of D and H respectively at 60x magnification. A white arrow in the panel of D denotes p63 positive basal progenitors in control embryos. On the other hand, no p63+ progenitors are identified in the epithelial layer of the Shhcre;Lats mutant VFs at P0 (G,H). Primary antibodies are color-coded according to their secondary antibodies, and nuclei are counterstained with DAPI (blue). IF images were taken at 20X and 60X magnification. Scale bars of 200um and 20um were used in figure panels.
Abbreviation: EP, epithelium; BC, basal cells; ApC, apical cells.