Figure 2. Bigenic mice (KMDAKT) for renal tubule-specific mitochondria-targeting of a dominant negative AKT1.
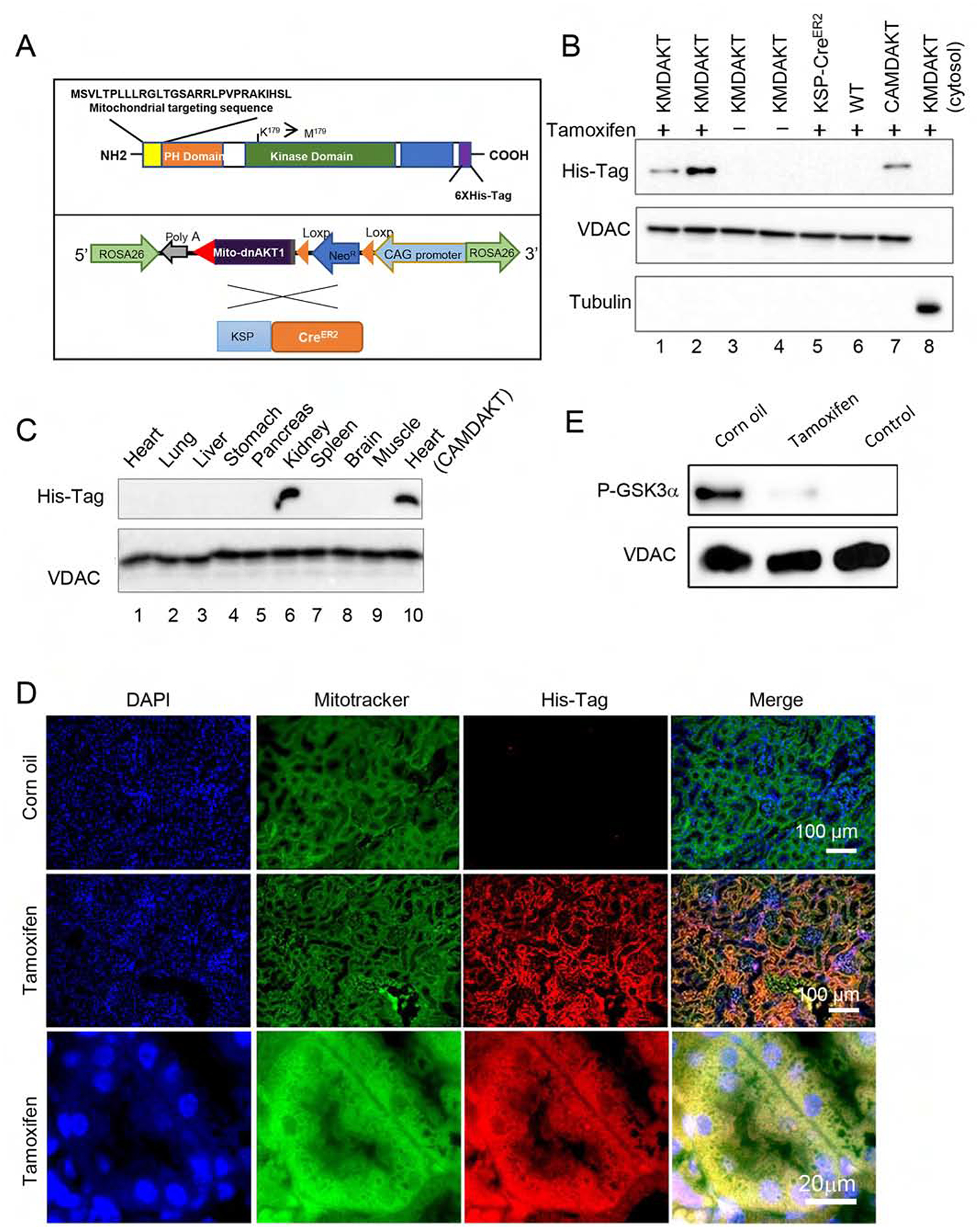
(A) Mitochondrial-targeting dominant negative AKT1 (mdnAKT) was engineered as described in Materials and Methods. A 6X His tag was added to the C terminus of AKT1 cDNA. mdnAKT transgenic mice were crossed with KSP-CreERT2 mice (Cre recombinase in renal tubular epithelial cells) to generate bi-genic mice (KMDAKT) for this series of experiments. (B) Expression of mdnAKT. Eight-week-old KMDAKT mice were injected with tamoxifen (TAM) or corn oil. The mitochondrial fraction was isolated and expression of mdnAKT proteins was analyzed by western blotting. The mdnAKT protein was expressed in the renal mitochondria isolated from Tam-treated KMDAKT mice but not in corn oil-treated KMDAKT mice, TAM-treated KSP-CreERT2 mice or TAM-treated wildtype (WT) mice. No mdnAKT was present in the renal cytosol fraction (last lane). VDAC was used as loading control and mitochondria marker, while tubulin is a cytosolic marker. (C) After TAM injection, the mitochondrial fraction was isolated from different organs and mutant AKT was only expressed in the kidney. The mdnAKT in the cardiac mitochondria of TAM-injected heart-specific mdnAKT mice (CAMDAKT) served as a positive control. (D) Mutant AKT1 co-localized to mitochondria in the renal tubules, immunofluorescence with anti-His-Tag antibody and MitoTracker® Green FM. (E) AKT activity in the mitochondrial protein preps were analyzed by an in vitro kinase assay using recombinant GSK3α as substrate. Tubular mitochondrial AKT was activated by IRI (corn oil injected), but AKT activity was inhibited in the Tam-treated KMDAKT mitochondria after IRI. The supernatant of KMDAKT mitochondria proteins after clearing immunoprecipitation with AKT antibodies served as negative control (lane 3).
