Fig. 1. Properties of PTPδ splice variants to induce postsynaptic differentiation.
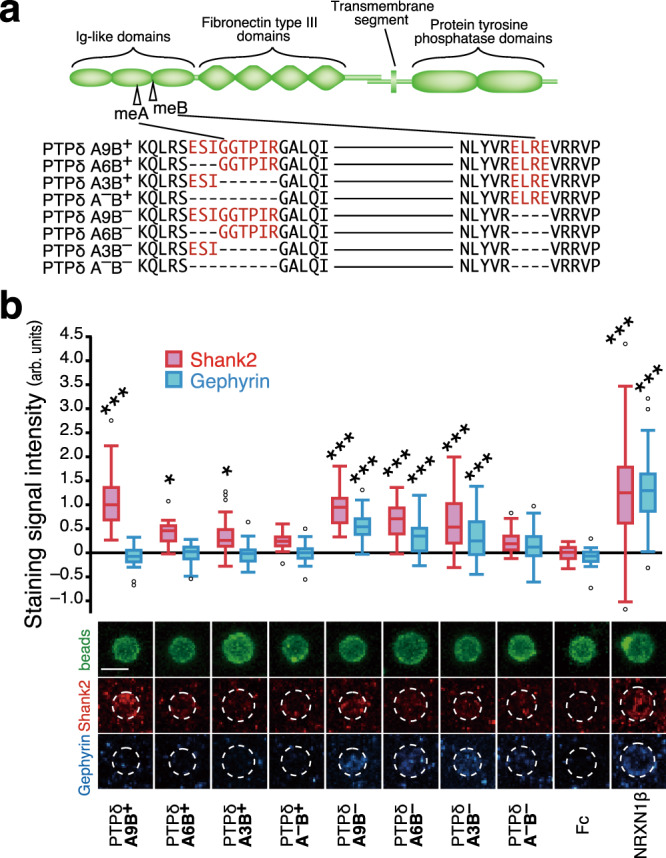
a Schematic structure of PTPδ and amino acid sequences of splice variants in Ig-like domains. me A and B sequences are colored in red. b Induction of postsynaptic differentiation of cerebral cortical neurons by beads conjugated with ECDs of PTPδ splice variants. Excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic terminals were visualized by immunostaining for Shank2 (red) and gephyrin (blue), respectively (bottom). Shank2 (red bars) and gephyrin (blue bars) staining signals on the beads (n = 35, 35, 37, 38, 35, 35, 36, 35, 35, and 35 for PTPδ A9B+, A6B+, A3B+, A–B+, A9B–, A6B–, A3B–, A–B–, Fc, and NRXN1β beads, respectively) were quantified (top). Scale bar, 5 μm. Data are presented as box plots. Horizontal line in each box shows the median, the box shows the interquartile range (IQR) and the whiskers are 1.5 × IQR. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001, Tukey’s post hoc test compared to control Fc beads. See Supplementary Table 4 for additional statistics and exact p values.
