Figure 1.
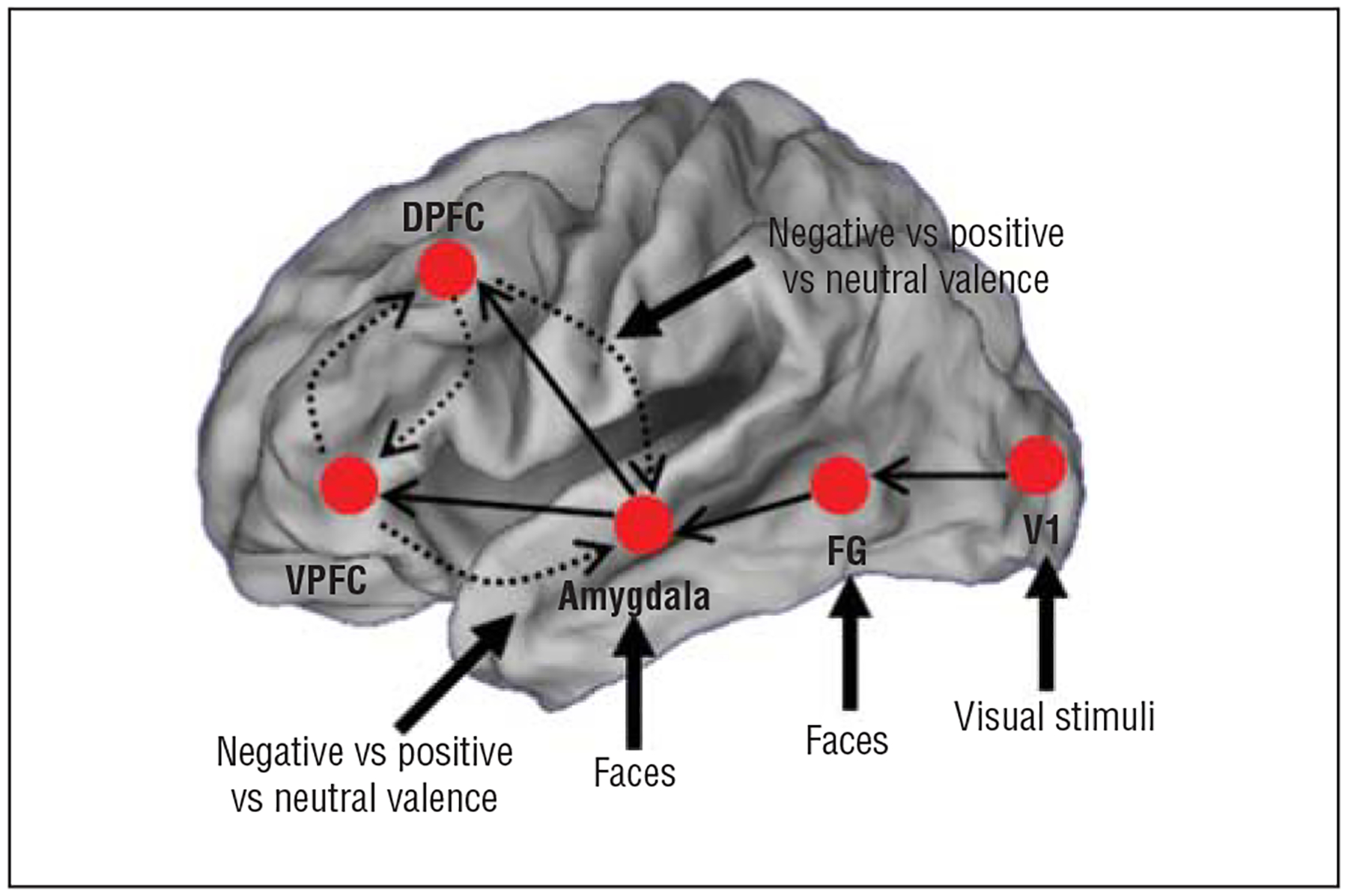
Summary of the general model architecture from which the dynamic causal models were constructed, based on a schematic network summarized in eFigure 1. Driving inputs to specific regions of interest were fixed across all models evaluated. All intrinsic connections are directional. Solid arrows depict fixed connections across all evaluated models. Dashed arrows depict conditions that were varied across models to assess the necessity of frontolimbic connections. Contextual modulation of frontolimbic connections by facial valence was also varied across models (all combinations of positive, neutral, and negative valences) in models in which intrinsic connections exist (see the “Methods” section for details). DPFC indicates dorsal prefrontal cortex; FG, fusiform gyrus; V1, primary visual cortex; and VPFC, ventral prefrontal cortex.
