Figure 6.
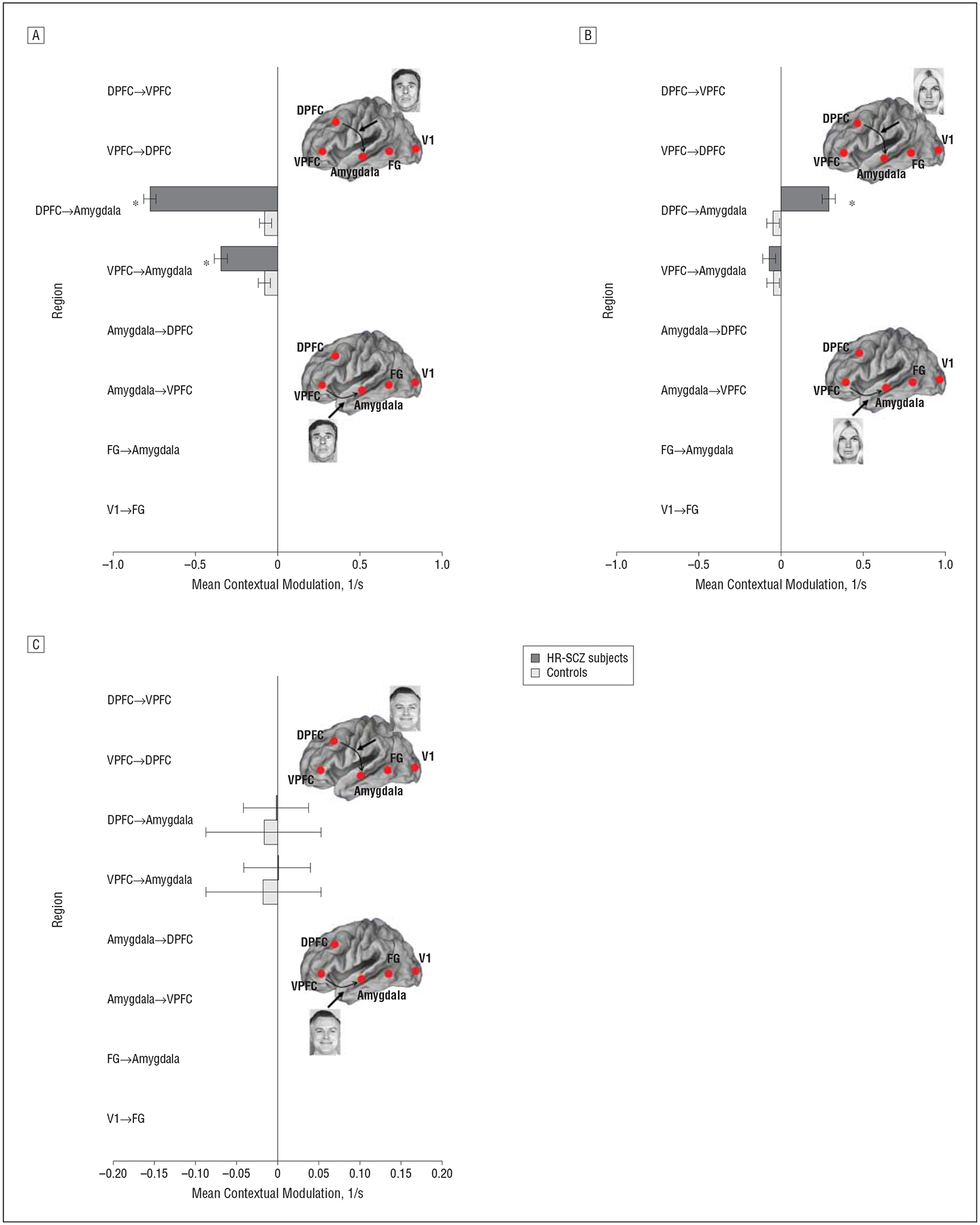
Contextual modulation by valence of frontolimbic pathways for control subjects and children and adolescent offspring of patients with schizophrenia (HR-SCZ subjects) for the winning model depicted in Figure 3C. A, Negative valence. B, Neutral valence. C, Positive valence. Denoted coupling parameters of the controls and HR-SCZ subjects are significantly different (*P=.01, Bonferroni corrected) (t statistics are provided in eTable 3). In the HR-SCZ subjects, we observed significantly increased inhibition by negative valence of DPFC-to-amygdala and VPFC-to-amygdala connections. No intergroup differences are observed for positive valence. Significantly increased excitation of the DPFC-to-amygdala pathway is observed for neutral valence. DPFC indicates dorsal prefrontal cortex; FG, fusiform gyrus; V1, primary visual cortex; and VPFC, ventral prefrontal cortex.
