Fig. 2. Genetic and chemical inhibition of DDR2 rescued ferroptosis in recurrent tumor cells.
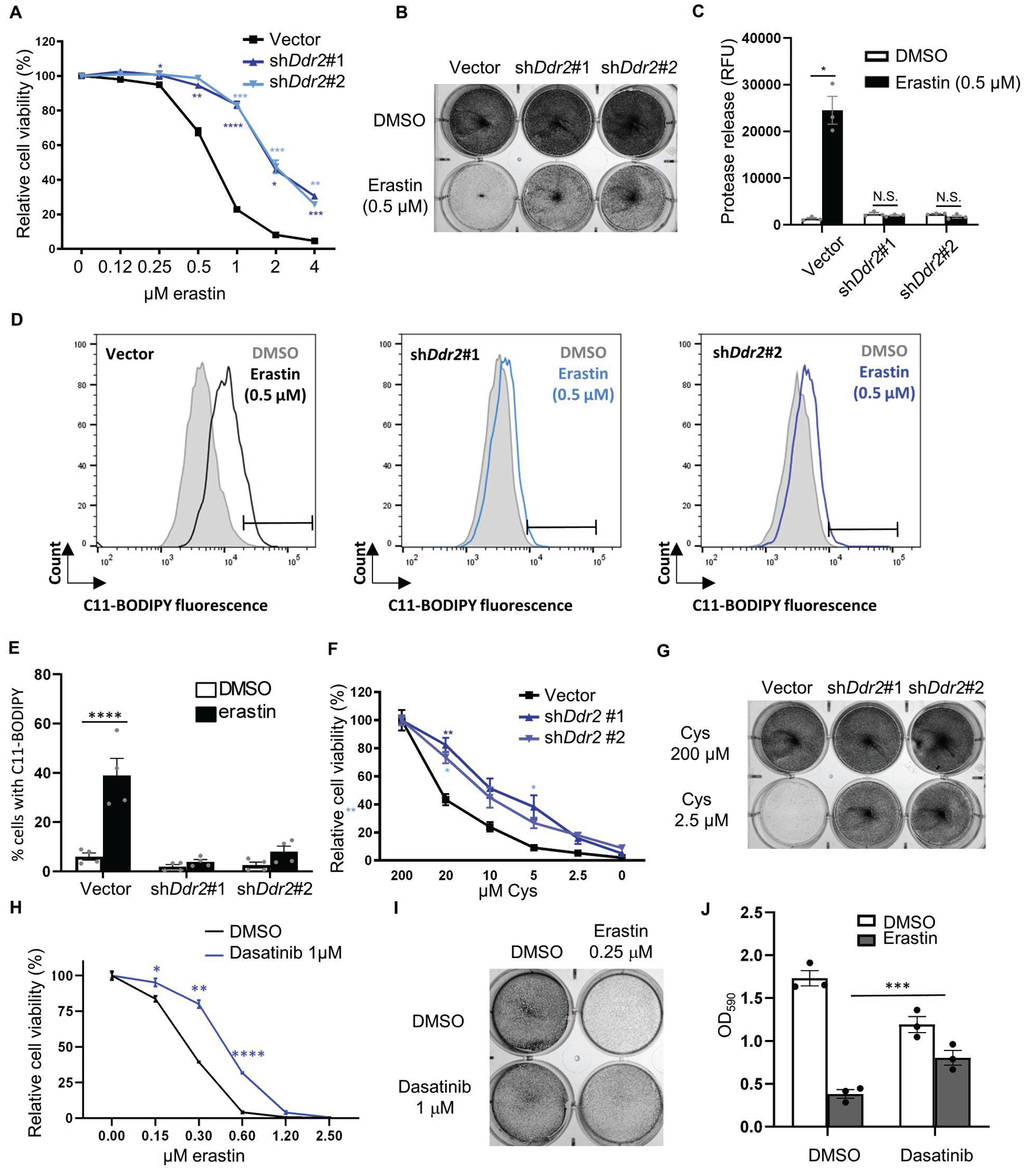
(A-E) Ddr2 knockdown rescued ferroptosis triggered by erastin. Recurrent tumor cells transduced with control or two Ddr2 shRNAs were treated with erastin for 19 hours and the cellular viability was determined by CellTiter Glo (A) and crystal violet staining (B). The effects on cell death were determined by CellTox Glo (C) and lipid peroxidation by C11-BODIPY staining (D, E). Representative data from one out of four independent experiments are shown (D). Quantification of lipid peroxidation in (E). (F-G) DDR2 knockdown rescued the reduction in cell viability triggered by cystine deprivation. Recurrent tumor cells transduced with control or Ddr2 shRNAs were treated with cystine deprivation and the cell numbers were determined by CellTiter Glo after 18 hours of incubation (F) or crystal violet staining after 16 hours of incubation (G). (H-J) DDR2 inhibitor, dasatinib (1 μM), rescued cell death triggered by erastin. Recurrent tumor cells were treated with dasatinib, erastin alone or in combination, and rescue effects of dasatinib were determined by CellTiter Glo (H), crystal violet staining (I), quantification of crystal violet (J). (A, F, H) n=3 biological replicates. (A, C, E, F, H, J) Two-way ANOVA, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. Bars show S.E.M.
