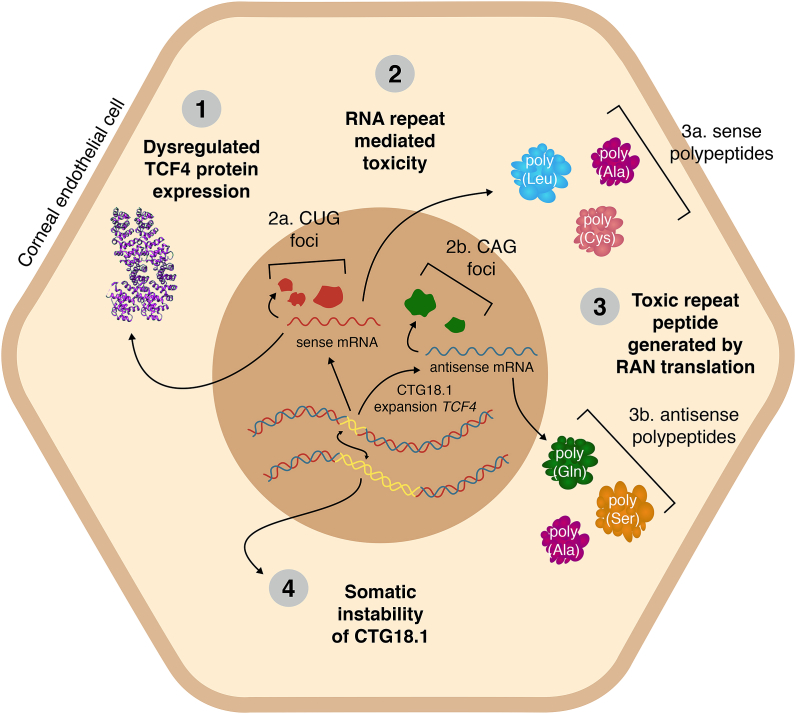
Fig. 3.
Mechanisms of cellular dysregulation associated with CTG18.1 expansions. Four non-mutually exclusive mechanisms have been proposed to drive and/or exacerbate the onset of CTG18.1 expansion-mediated FECD, including; (1) dysregulated expression of TCF4 transcripts, (2) accumulation of toxic (a) sense (CUG)n and (b) antisense-derived (CAG)n repetitive RNA transcripts, (3) RAN translation of repetitive RNA transcripts, and (4) age and tissue-dependant somatic instability of the repeat element.