FIGURE 3.
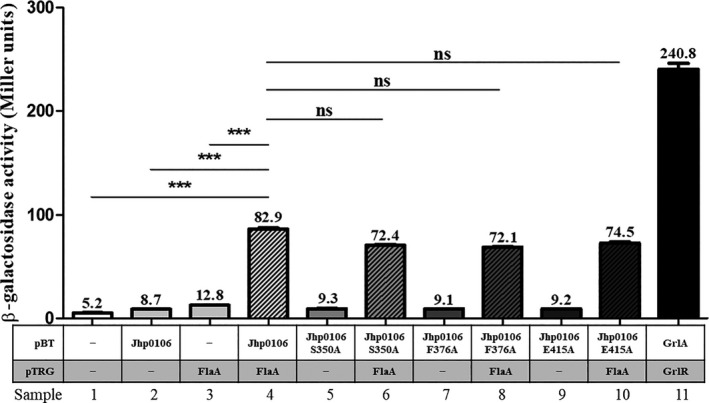
The Jhp0106‐FlaA interaction assessed by a bacterial two‐hybrid system. Jhp0106‐FlaA protein interaction was investigated using a bacterial two‐hybrid system in E.coli. The gene flaA was cloned into pTRG to determine whether FlaA interacts with Jhp0106 and the Jhp0106‐derivatives carrying S350A, F376A, or E415A mutation that were cloned in pBT. E.coli cells harboring empty vectors pBT (bait) and pTRG (target) (sample 1) served as negative control. In parallel, E.coli cells harboring only pBT‐Jhp0106 (sample 2), pTRG‐FlaA (sample 3), pBT‐Jhp0106::S350A (sample 5), pBT‐Jhp0106::F376A (sample 7), or pBT‐Jhp0106::E415A (sample 9) served as background signal controls. For positive control, E.coli cells obtained both pBT‐GrlA and pTRG‐GrlR (sample 11). An increase of measured β‐galactosidase activity is an indication of positive interaction between the tested target and bait proteins (samples 4, 6, 8, and 10). The results were the representative of three independent experiments (means ±SEM). *** denotes statistical significance with p < 0.001; ns stands for “not significant.”
