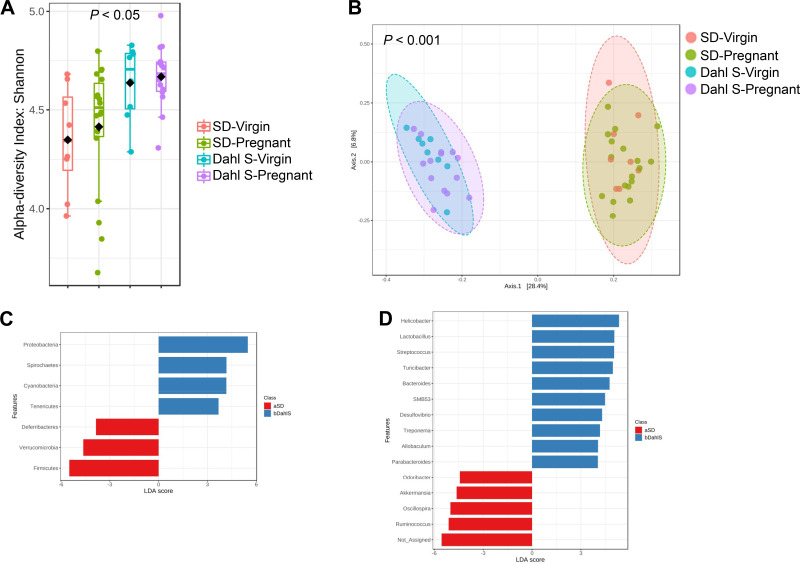
Figure 1.
Female Dahl S and SD rats have distinct taxonomic composition and phylogenetic diversity at baseline. A: α diversity presented as Shannon index. Each dot represents an individual rat. Pink bars represent virgin SD; green bars represent SD rats that were later mated; blue bars represent virgin Dahl S; and purple bars represent Dahl S rats that were later mated. B: PCoA plot representing β-diversity, each dot represents an individual rat. The distance between the two clusters indicates that the microbial population is significantly distinct between strains. The pink ellipse represents virgin SD; the green ellipse represents SD rats that were later mated; the blue ellipse represents virgin Dahl S; and the purple ellipse represents Dahl S rats that were later mated. C: LEfSe bar plot of differentially abundant phyla. Blue bars represent phyla that are more abundant in Dahl S and red bars represent phyla that are abundant in SD. D: LEfSe bar plot of differentially abundant genera. Blue bars represent genera that are more abundant in Dahl S and red bars represent genera that are more abundant in SD. n = 6 or 10 female rats. Dahl S, Dahl salt-sensitive; LEfSe, linear discriminate analysis effect size; PCoA, principle coordinates analysis; SD, Sprague Dawley.