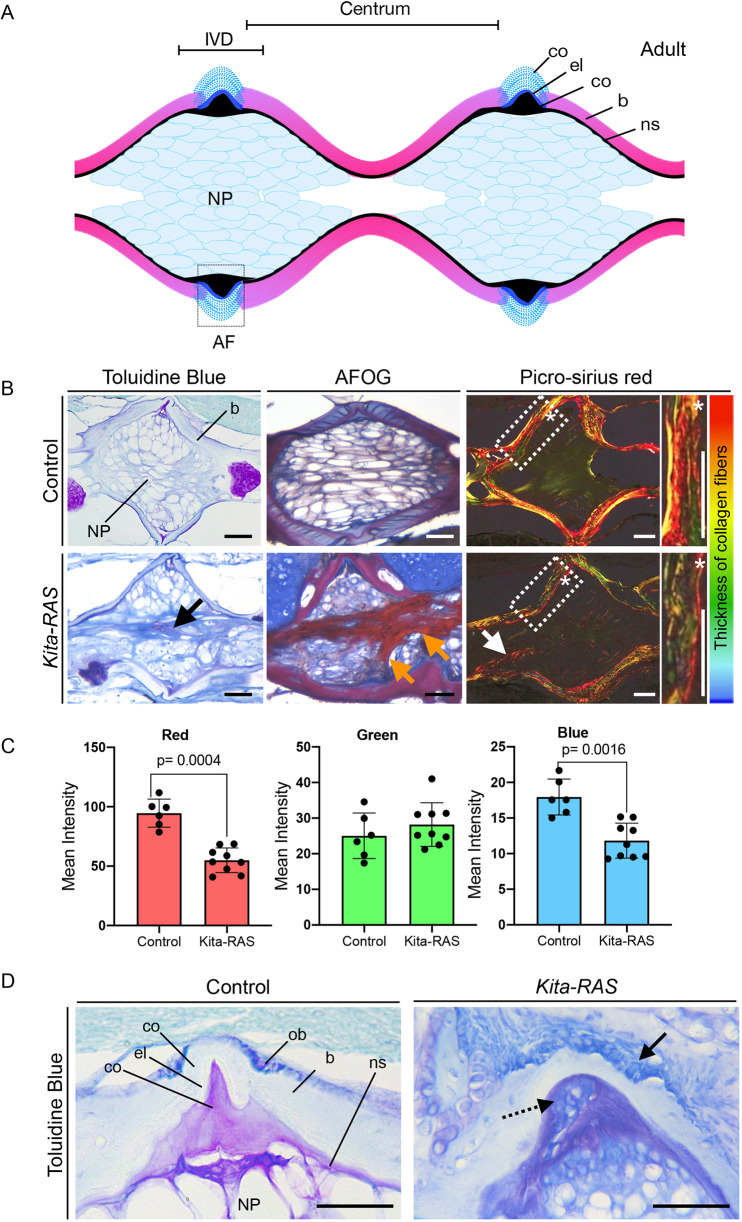
Fig. 7.
Fibrotic nucleus pulposus and abnormal annulus fibrosus in kita-RAS resemble intervertebral disc degeneration. (A) Schematic of a histological section of the vertebral column of zebrafish (off from the midline) showing two consecutive IVDs. AF, annulus fibrosus; b, bone; co, collagen layers; el, elastin layer; IVD, intervertebral disc; NP, nucleus pulposus; ns, notochord sheath. (B) Histological sections of adult control (kita-mCherry) and kita-RAS fish stained with Toluidine Blue (morphology), AFOG (fibrosis) and Picro-Sirius Red (fibrosis and collagen fibre thickness). Bone (b) and inner nucleus pulposus (NP) are indicated on the control Toluidine Blue picture. Abnormal fibrosis (black, orange and white arrows), cellularity and disorganisation of the NP were detected in kita-RAS fish. The regions within the dashed line boxes (Picro-Sirius Red staining) are shown at higher magnification to show the bone in detail. Asterisks were added to help with orientation, and they show the same position in lower- and higher-magnification pictures. Poor quality of bone can be measured by the tones of colours from Picro-Sirius Red staining. Thicker fibres are red and thinner fibres are blue/green (colour bar). (C) Collagen fibre quantification was performed by determining the means of pixel colours (red, green and blue) in the Picro-Sirius Red staining pictures. Note a reduction of thick (red) and very thin (blue) fibres in kita-RAS (n=9 vertebrae, n=3 fish) in comparison to controls (n=6 vertebrae, n=3 fish). Unpaired, nonparametric t-test and Mann–Whitney test were used. Data are mean±s.d.; P-values are indicated when significant (P<0.05). (D) Toluidine Blue staining to show details of the AF area in control (kita-mCherry) and kita-RAS. Note the loss of the layers of collagen and elastin in kita-RAS and disorganised and higher number of osteoblasts (arrow). Internal collagen layer is mixed with abnormal cells (dashed line arrow). Scale bars: 50 µm.