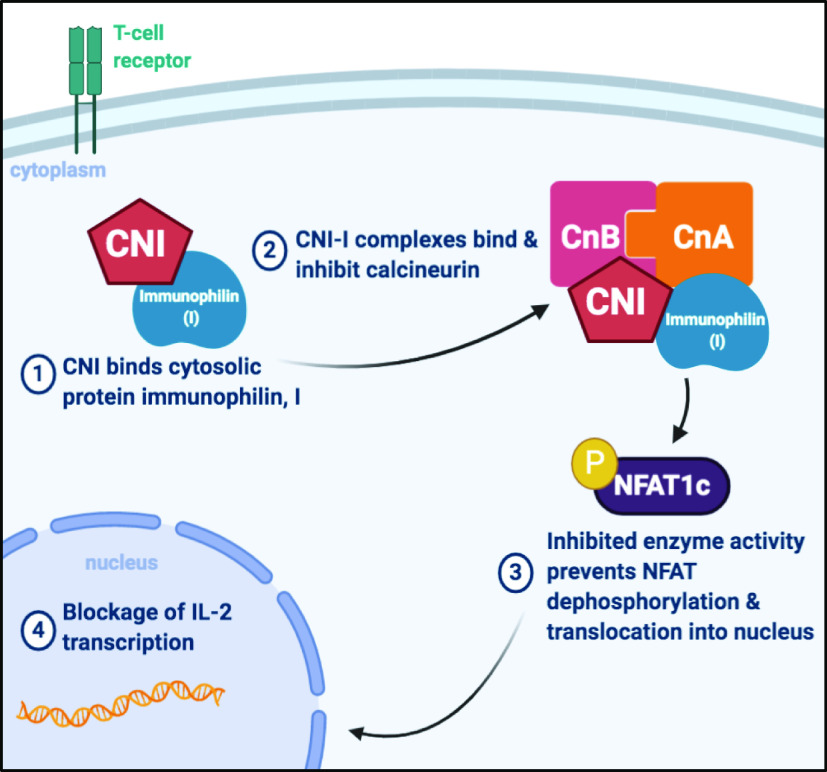
Figure 1.
Calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs) blunt the immune response by inactivating calcineurin phosphatase activity. CNIs bind to cytosolic proteins called immunophilins (I) (step 1) enabling the CNI-I complex to bind calcineurin active site, thereby inhibiting phosphatase activity (step 2). Upon inhibition, transcription factors such as nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) are unable to become activated by dephosphorylation (step 3). This prevents NFAT translocation into the nucleus to increase IL-2 transcription (step 4), thereby blunting immune activation. [Image created with BioRender.com.]