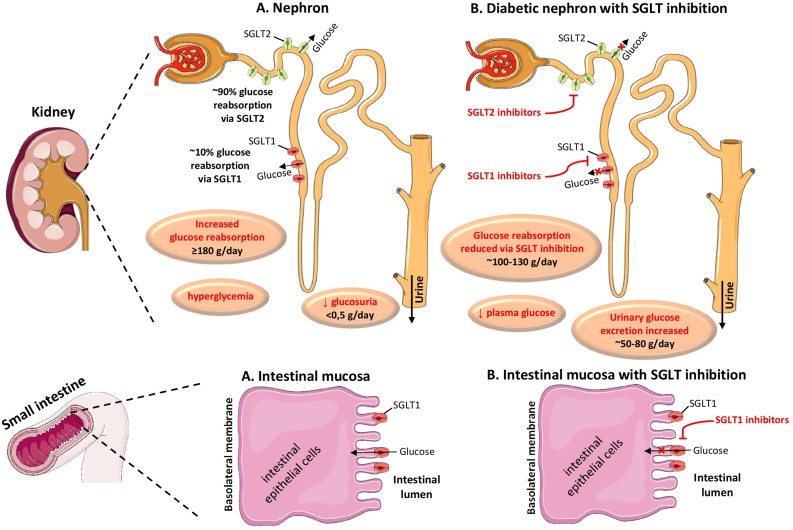
Fig. 1.
SGLTs; Sodium Glucose Co-transporters.
SGLT1 and SGLT2 are proteins found in the intestinal mucosa of the small intestine (SGLT-1) and the proximal tubule of the nephron (SGLT1 and SGLT2) playing an important role in maintaining blood glucose balance. In physiologic conditions, SGLT1 is responsible for glucose absorption in the small intestine, and for the reabsorption of nearly 10% of the filtered glucose load, while SGLT2 is responsible for approximately 90% of the kidney’s glucose reabsorption. The selective SGLT2 inhibitors empagliflozin, canagliflozin, dapagliflozin and ertugliflozin act by inhibiting SGLT2 in the kidney, while the dual SGLT1 and SGLT2 inhibitor sotagliflozin acts by inhibiting both renal SGLT2 and intestinal SGLT1.
(All images are derived from the free medical site http://smart.servier.com/by Servier licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License).