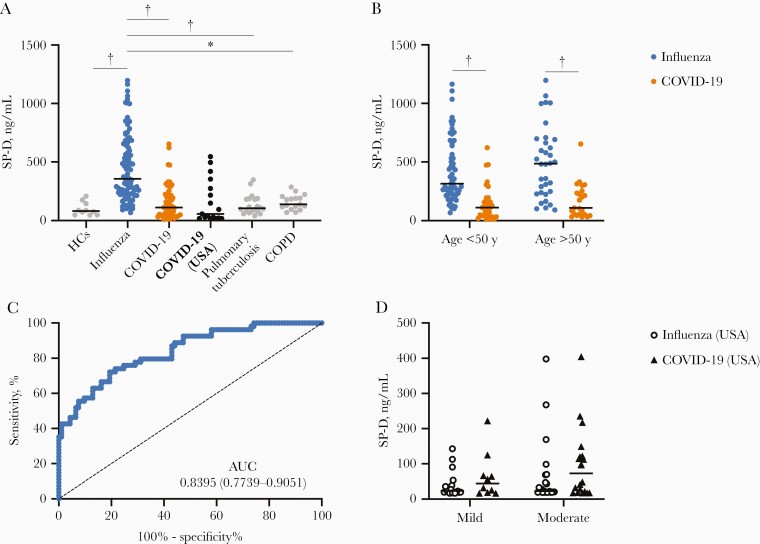
Figure 1.
Surfactant protein D (SP-D) differentiates pandemic influenza from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in patients with severe disease. A, Serum levels of SP-D were determined in healthy controls (HCs; n = 10) and patients with severe pandemic influenza A(H1N1) (n = 93), severe COVID-19 (n = 54), pulmonary tuberculosis (n = 20), or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD; n = 17). Plasma SP-D levels were also analyzed in a validation cohort of patients with severe COVID-19 from St Louis, Missouri (n = 17). *P < .01; †P < .001 (Kruskal-Wallis test/post hoc Dunn test). B, Serum SP-D levels in patients with severe pandemic influenza or COVID-19 stratified by age. †P < .001 (Mann-Whitney U test). C, Receiver operating characteristic curve of the serum SP-D levels in patients with severe pandemic influenza or COVID-19. Abbreviation: AUC, area under the curve. D, Analysis of plasma SP-D levels in the validation cohort of patients with seasonal influenza or COVID-19 with mild (n = 18 [influenza] vs 10 [COVID-19]) or moderate disease (n = 23 vs 20) (compared using Mann-Whitney U test). Graphs display medians with interquartile ranges or the AUC and 95% confidence intervals.