FIGURE 2.
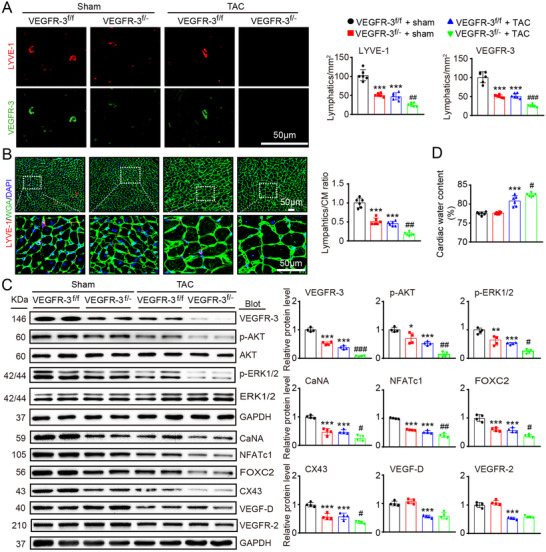
Knockdown of VEGFR‐3 impairs cardiac lymphangiogenesis and causes edema after pressure overload. VEGFR‐3 knockdown (VEGFR‐3f/−) mice and their WT (VEGFR‐3f/f) littermates were subjected to sham or TAC surgery and remained under sham or TAC conditions for 6 weeks. (A) Heart sections stained with an antibody against LYVE‐1 (red) or VEGFR‐3 (green) (left, scale bar: 50 μm) and quantification of LYVE‐1+ or VEGFR‐3+ lymphatic vessels (right, n = 6). (B) Heart sections stained with an anti‐LYVE‐1 antibody (red), TRITC‐labeled WGA (green) and DAPI (blue) (left, scale bar: 50 μm) and the LYVE‐1+ vessel to CM ratio (right, n = 6). (C) Immunoblot analysis of the VEGFR‐3, p‐AKT, AKT, p‐ERK1/2, ERK1/2, calcineurin A (CaNA), NFATc1, FOXC2, CX43, VEGF‐D, and VEGFR‐2 proteins in the heart (left) and quantification of these proteins (right, n = 4). GAPDH was used as an internal control. (D) Gravimetric assessment of the cardiac water content (%) as determined by the cardiac dry weight‐to‐wet weight ratio (n = 6). The data are presented as the mean ± SD, and n represents the number of animals per group. Statistical analysis was performed with one‐way ANOVA; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 versus VEGFR‐3f/f + sham; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, and ### p < 0.001 versus VEGFR‐3f/f + TAC
