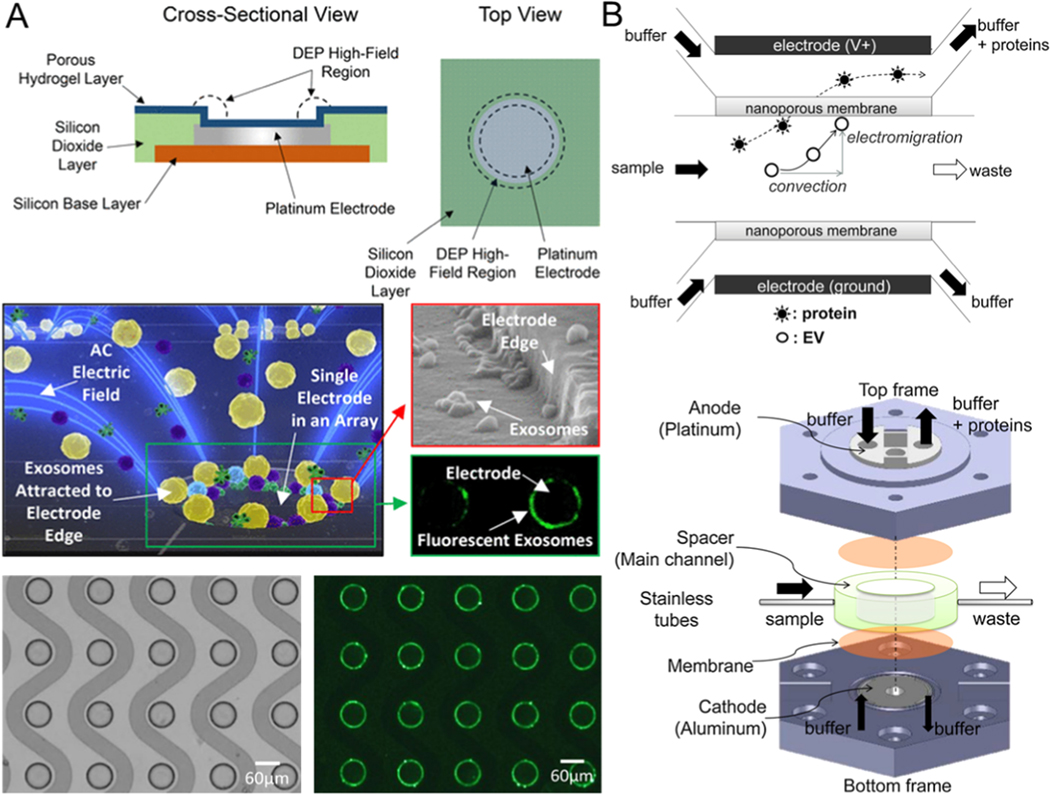
Figure 6.
Microfluidic exosome isolation based on dielectrophoretic. (A) Dielectrophoresis-driven exosomes isolation by the microfluidic device composed of the microarray of ACE. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [115]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (B) Schematic of microfluidics combined with a filtration system to isolate exosomes by electrophoretic force. Proteins smaller than the membrane pore size can be propelled through the membrane while EVs larger than the membrane pore size cannot diffuse into the membrane and are captured on the nanoporous membrane. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [59]. Copyright 2016, Elsevier.