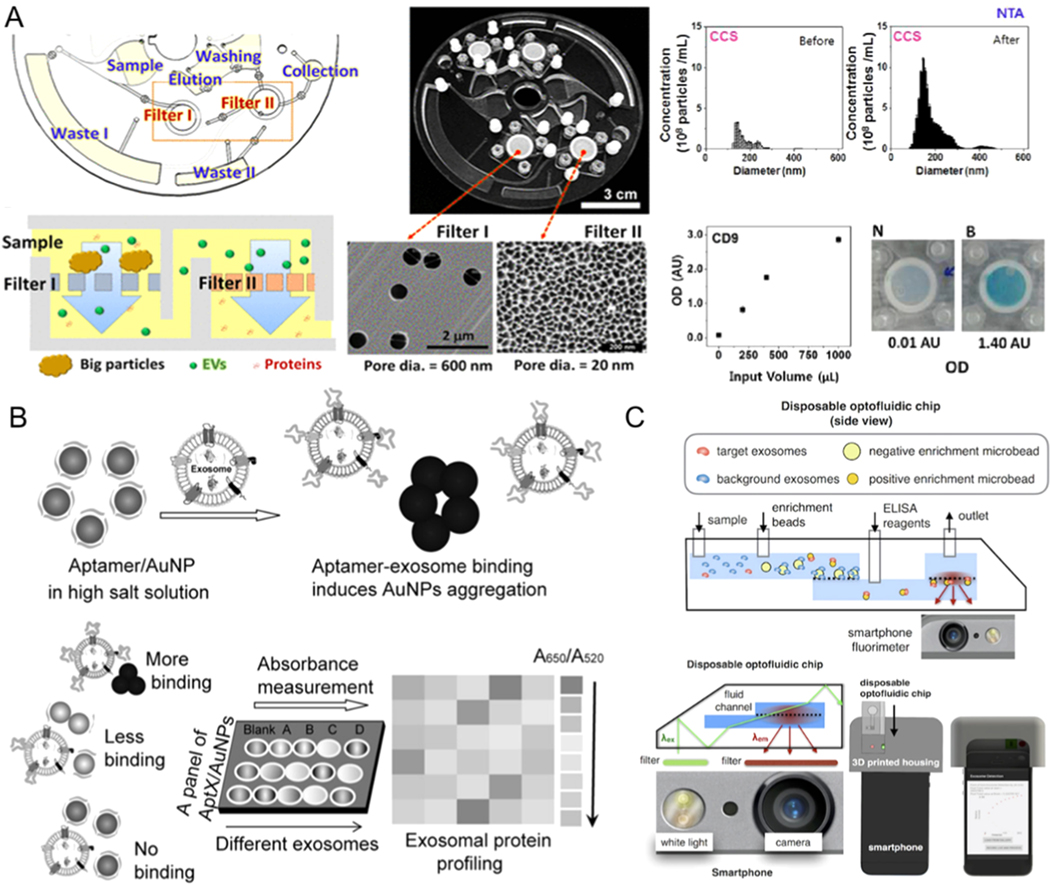
Figure 7.
Microfluidic exosome detection based on colorimetric mechanisms. (A) The microfluidic device combined with filter for exosome isolation and detection using ELISA. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [60]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (B)Biosensor for colorimetric profiling of exosomal proteins. The binding of exosomes with aptamer/gold nanoparticles complex in the high salt solution can induce the aggregation of gold nanoparticles and cause the absorbance displacement. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [125]. Copyright 2017, Wiley. (C) Schematic illustration of microfluidic-based mobile exosome detector (μMED). The quantitative data can be read with the camera of the smartphone. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [127]. Copyright 2016, Nature Publishing Group.