Table 1.
Current conventional exosome isolation methods.
| Isolation technique | Principle | Time | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Differential ultracentrifugation
|
Particles with various size and density demonstrate various sediment speed under centrifugation | 5–18 hours | ✓ Suitable for large volume preparation | ➣Require expensive equipment ➣Potential damage because of the high-speed centrifugation ➣Time-consuming |
Size
|
Separate with specific molecular size exclusion | 2–4 hours | ✓ Isolate native exosomes | ➣ Exosomes and proteins clogging on nanopores ➣ Potential isolate other nanovesicles in similar size with exosomes |
Bead
|
On the basis of interaction between antibodies/ligan ds and exosome markers | 2–6 hours | ✓ High-purity ✓ Useful for isolating specific exosomes from target origin |
➣Expensive antibodies functionalization ➣Low yields and processing volume ➣Exosome markers must be optimized |
Polymer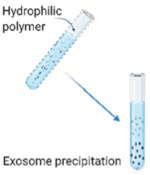
|
High hydrophilic water-excluding polymers changes the solubility of exosomes | 0.5–12 hours | ✓ Available for all types of samples ✓ Easy to use |
➣Potential polymeric, protein aggregates, and other extracellular vesicles contaminants. |
