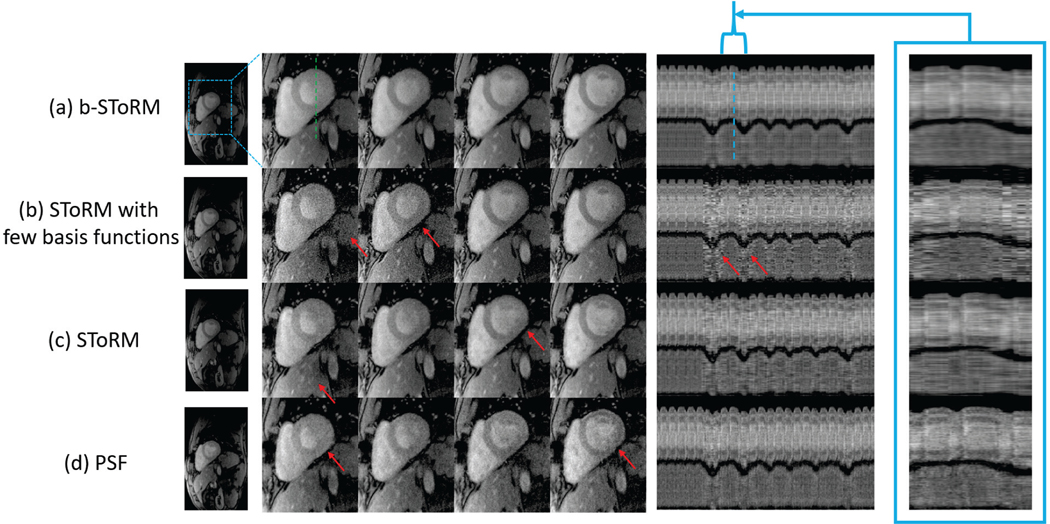
Fig. 4:
Comparison with other methods. Few frames and temporal profiles are shown from a dataset reconstructed using (a) b-SToRM (b) SToRM using few basis functions (c) SToRM [12] (d) PSF scheme [22]. It is observed that b-SToRM yields the best overall results, followed by SToRM that shows some degradation in image quality indicated by the red arrows. Note that b-SToRM also benefits from a speed-up due to the factorization of the Casorati matrix. It is also observed from (b) that using a few basis functions of the SToRM Laplacian matrix results in artefacts in the images and the temporal profile. Specifically, the approximation of the SToRM Laplacian matrix using few basis functions is poor, which translates to poor recovery. The PSF method also shows some image artefacts as compared to b-SToRM, which shows the benefit of the non-linear manifold modeling over subspace approximation. The red arrows in the figure point to artefacts in the images reconstructed using the competing methods. Similar results on an additional dataset are included in the supplementary material.