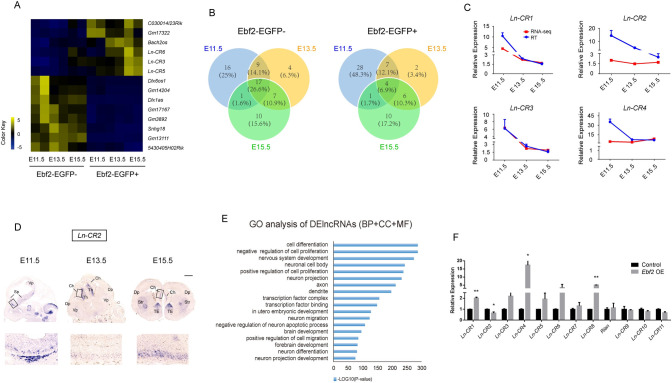
Fig 3. Characterization of differentially expressed lncRNAs in the Ebf2-EGFP+ and Ebf2-EGFP- cells.
(A) Heatmap representing all differential expressed lncRNAs (FDR<0.05, p-value<0.05) in Ebf2-EGFP+ & Ebf2-EGFP- cell samples at the three embryonic stages. (B) Venn diagram displaying the extent of overlapping between DElncRNAs at the three embryonic stages. (C) The expression pattern of DElncRNAs between Ebf2-EGFP+ or Ebf2-EGFP- cells is consistent revealed by RNA-seq and qRT-PCR. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 3 independent experiments). (D) In situ hybridization showing the endogenous expression of CR-specific lncRNA Ln-CR2 at E11.5, E13.5 and E15.5, respectively. Regions with specific expression are labeled and higher magnification images of boxed areas are shown below. Abbreviations: Sp, septum; Vp, ventral pallium; Th, thalamus; Dp, dorsal pallium; Ch, cortical hem; Str, striatum; TE, thalamus eminence. Scale bar, 900 μm. (E) Enriched functional assessments (including biological processes, cellular components and molecular function) of highly expressed DElncRNAs (fold change ≥ 2) in Ebf2-EGFP+ or Ebf2-EGFP- cell population. (F) qRT-PCR analysis comparing the expression levels of lncRNAs in primary neural cell culture assay after virus infection with control (H1) or Ebf2-overexpression. Data represent mean ± SEM (n = 4 independent experiments, *P<0.05, Student’s T test).