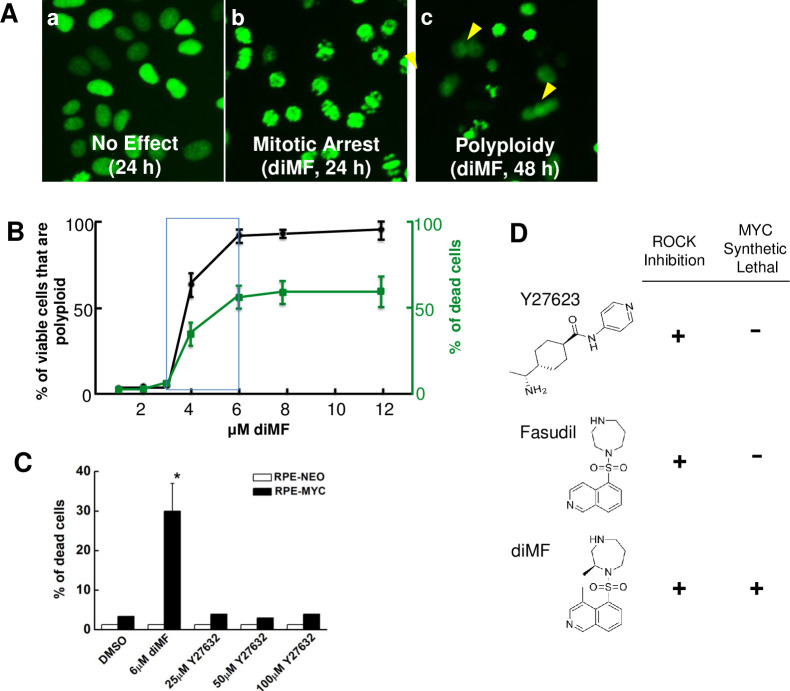
Fig 1. diMF elicits MYC-dependent cytotoxicity.
Representative images (A) of RPE-MYCH2B-GFP cell phenotypes observed with high-content screening with a small molecule library. Shown are (a) cells treated with DMSO as a negative control, (b) cells mitotically arrested after 24 hours of diMF (10 μM) and (c) polyploid cells (arrowheads) that formed after 48 hours of diMF. (B) Concentration-response between diMF and the percentage of non-viable cells after 48 hours (green) and percentage of the remaining cells that are polyploid (black). Data points are derived from experiments done in triplicate from 3 independent experiments (n = 9) and error bars represent standard deviation. (C) RPE-NEO and RPE-MYC cells were treated with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO), diMF (6 μM) or varying concentrations of the ROCK inhibitor Y27623 for 48 hours. Cell viability was assayed by trypan blue exclusion assay. Viability differences between RPE-NEO and RPE-MYC cells with each chemical were statistically compared using two tailed, unpaired t-tests. The symbol * indicates p<0.01. (D) Comparison of the chemical structure and functional activity of ROCK inhibitors.