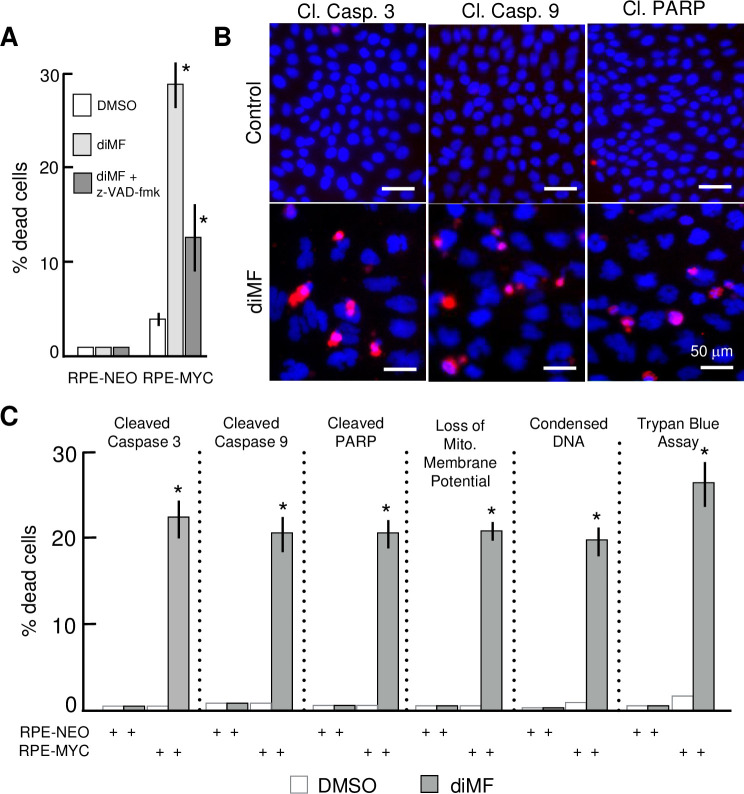
Fig 3. MYC-diMF engages the intrinsic apoptotic cascade for synthetic lethality.
(A) Partial inhibition of MYC-diMF synthetic lethality by the caspase inhibitor z-VAD-fmk. RPE-NEO and RPE-MYC cells were treated for 72 hours with 0.1% DMSO (), 6 μM diMF (), or 6 μM diMF + 100 μM z-VAD-fmk (). Statistical analysis was with one-way AVOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. The symbol * indicates p<0.01 when compared with the DMSO control group. (B) Immunofluorescent staining for cleaved (activated) caspase 3, cleaved caspase 9 and cleaved PARP in RPE-MYC cells treated with 0.1% DMSO (top panels) or 6 μM diMF (bottom panels) for 3 days. Cells were stained for DNA with DAPI (blue). Micro-images were taken with an EVOS FL Auto microscope. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Percentage of cells positive for cell death markers in the indicated assays. RPE-MYC and RPE-NEO cells were treated with 0.1% DMSO (□) or 6 μM diMF () for 3 days and then subjected to the indicated viability assays. The experiment was done in triplicate so that n = 9 for each data point. Error bars represent standard deviation. The symbol * indicates p <0.01 when diMF treatment was compared with DMSO treatment (unpaired, 2-tailed t-test).