Figure 1. Overview of the cycle of alcohol addiction.
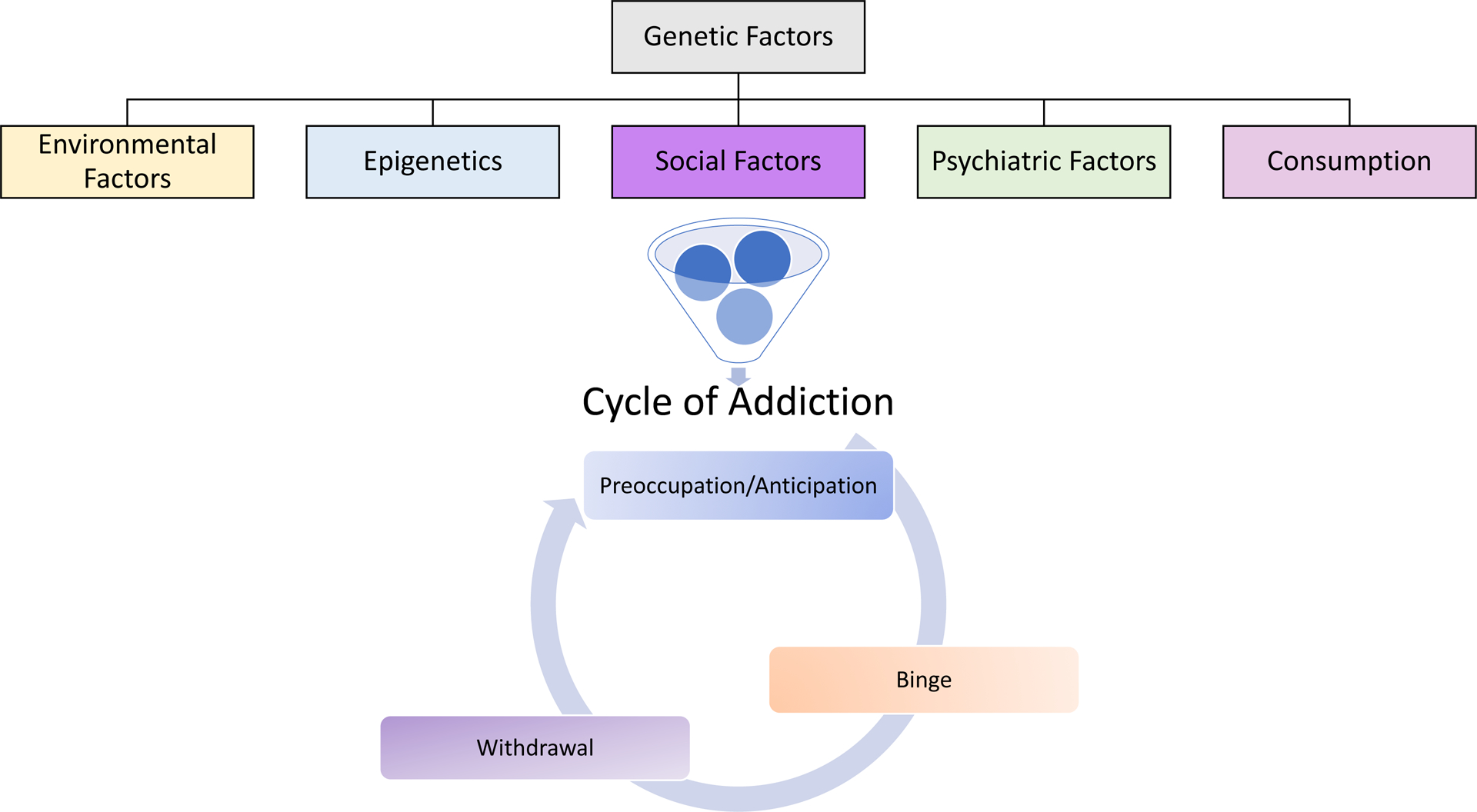
Prior to the first drink, several factors increase the risk of developing an AUD. These include genetic factors such as polymorphisms in aldehyde dehydrogenase, environmental factors such as education or social status, social factors such as if family members or friends consume alcohol, psychiatric factors such as comorbid disorders, (e.g. stress, anxiety, depression), or consumption factors such as age of onset. The cycle of addiction framework suggests that as the development of AUD occurs, individuals go through cycles of preoccupation and anticipation, binge consumption and then withdrawal, and that continued and persistent moves through this cycle eventually lead to a net affective disorder, where alcohol consumption is less for the rewarding effects and more to alleviate the negative effects (Koob and Volkow, 2016).
