Fig. 5. Clinical study on the hemostatic effect of CHI-C sponge in patients undergoing hepatectomy and a proposed hemostatic mechanism of CHI-C.
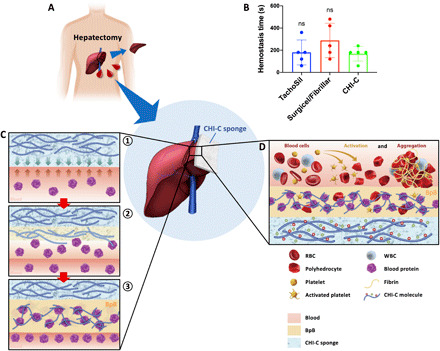
(A) A schematic illustration of the clinical trial design. A CHI-C sponge was applied for persistent local bleeding despite the first-line hemostatic procedures. (B) Hemostasis time (in seconds) results of the CHI-C sponge compared with the conventional hemostatic agents (TachoSil and Surgicel/Fibrillar). The data are presented as means ± SD, and comparisons were performed using the Mann-Whitney U test. (C) Schematic illustrations of the primary hemostatic mechanism of CHI-C, which forms physical barriers (BpB) by interacting with blood proteins: ① contact and dissolution of CHI-C at bleeding site, ② interaction of the dissolved CHI-C with blood proteins, and ③ rapid BpB (physical barrier) formation. (D) A schematic illustration of the secondary hemostatic mechanism of CHI-C, which activates and aggregates blood cells. WBC, white blood cell.
