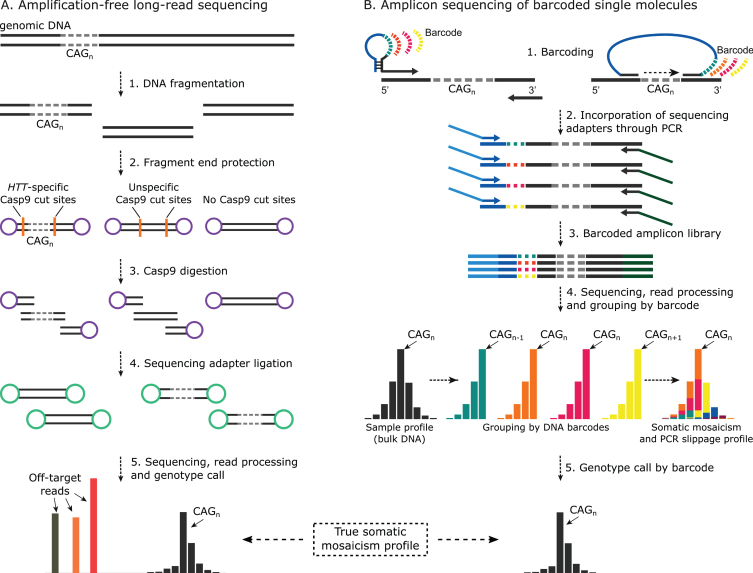
Fig. 7.
Method summary for somatic mosaicism quantification at the level of a single molecule in HD. A) Generalised schematics for CRISPR/Casp9-mediated targeted enrichment of HTT locus for single-molecule long-read sequencing (i.e., no-amp targeted sequencing). Following DNA fragmentation and DNA molecule protection by adapter ligation or de-phosphorylation, CRISPR/Cas9 and locus-specific guide RNAs are used to selectively cut across the region of interest. While undigested DNA fragment ends are still protected, sequencing adapters are ligated to the Cas9 digestion product. Sequencing is then done on the appropriate single-molecule long-read sequencing platform such as PacBio SMRT or Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT). No-amp targeted sequencing studies of repeat expansions have used one or two Cas9 cuts with PacBio sequencing [31, 49, 57, 59] or ONT sequencing [58] respectively. Single-molecule sequencing read output can then be used to build the somatic mosaicism profile. B) The general method for amplicon sequencing of barcoded single molecules. Several methods for single-molecule barcoding exist, including one-cycle PCR using hairpin-protected primers with degenerate tags or region capture by barcoded molecular inversion probes. Following barcoding, sequencing adapters are incorporated into the uniquely tagged molecules through PCR with overhang primers. The resulting amplicon library is then sequenced on the platform of interest, including Illumina MiSeq or PacBio, depending on the amplicon length and the desired throughput. Resulting reads are grouped by barcode family, and the repeat length of the original molecule for each family is determined to build the real somatic mosaicism profile per sample.