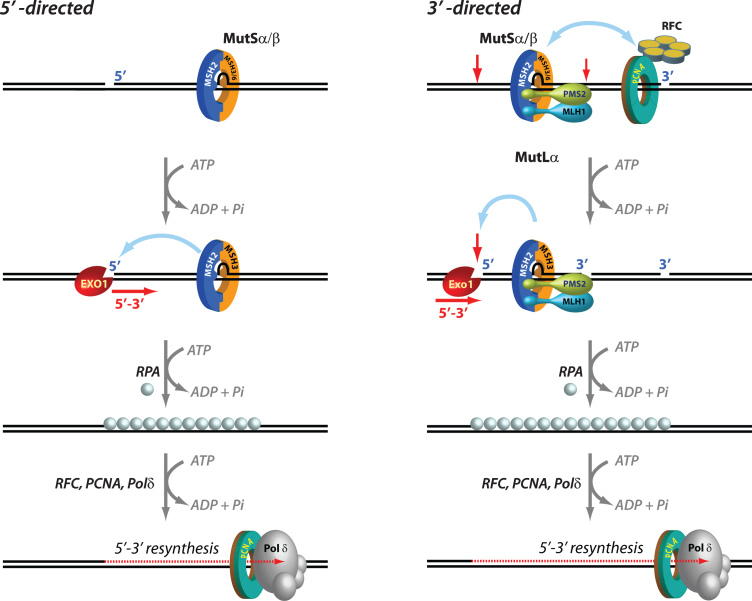
Fig. 1.
Mechanisms of 5′ and 3′ human mismatch repair. Distinct molecular mechanisms mediate mismatch repair, depending on strand-break polarity. Left, DNA mismatches or extrahelical extrusions are recognized by MutSα or MutSβ. When the strand-break is located 5′ to the mismatch, MutSα/β activates the processive 5′–3′ exonuclease activity of ExoI in an ATP-dependent manner. The ensuing gap is protected by the single-stranded DNA binding protein complex RPA, followed by DNA resynthesis across the gap by DNA polymerase δ, aided by the replication sliding clamp PCNA and the clamp loader RFC. Right, if the strand-break is located 3′ to the mispair, error correction relies on oriented loading of PCNA by RFC at the strand break. Thus, MutSα/β recruits MutLα in an ATP-dependent manner, resulting in the activation of a latent endonuclease function in MutLα in the presence of DNA-loaded PCNA. The additional strand-breaks catalyzed by MutLα bracket the mismatch, and facilitate processive 5′–3′ hydrolysis of the nicked strand by MutSα-activated ExoI. Gap protection and filling occur as in the 5′ nick-directed reaction.