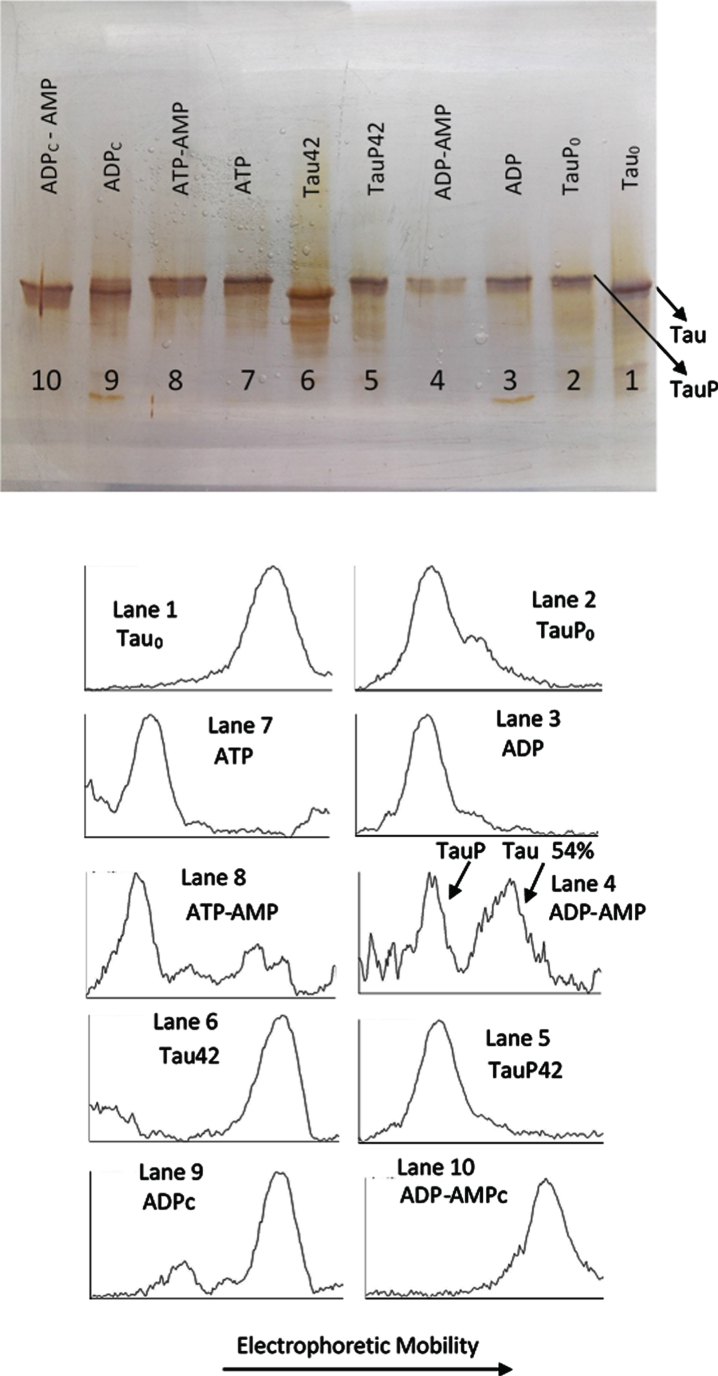
Fig. 4.
Silver stained of tau and phosphorylated tau separated by SDS-PAGE (8% acrylamide). Lanes 1, 6–10: Tau protein (3 μg/ml final concentration) was diluted in a buffer composed of 22.5 μl of 10 mM Hepes, 0.15 M KCl, 0.25 mM 2-mercaptoethanol, 15 mM MgCl2, and 0.1 mg/ml Ampicillin at pH 7 plus 2.5 μl of a solution of 250 mM potassium phosphate 10 mM and 0.1 mg/ml of Ampicillin at pH 7, containing 10 mM of P1, P5-Di(adenosine-5’) pentaphosphate. This solution was incubated with C-PKA, at 20°C for 42 h, in the presence of 2.5 mM ATP plus the presence (Lane 8) or absence (Lane 7) of 25 mM of AMP and in presence of 2.5 mM ADP plus the presence (Lane 10) or absence (Lane 9) of 25 mM of AMP. Lanes 1 and 6 are controls of tau in the absence of C-PKA and nucleotides, incubated for 0 h (Lane 1) and 42 h (Lane 2). Lanes 2-5: Phosphorylated tau (TauP) (2.7 μg/ml, final concentration) was diluted in the same buffer solution as described for tau and incubated with C-PKA, at 20°C for 42 h, in the presence of 2.5 mM ADP plus the presence (Lane 4) or absence (Lane 3) of 25 mM of AMP; dephosphorylation percentage of TauP is indicated. Lanes 2 and 5 are controls of TauP in the presence of 2.5 mM ADP but in the absence of C-PKA, incubated for 0 h (Lane 2) and 42 h (Lane 5). 5 units of C-PKA from Promega were used, when added. Both tau and TauP solutions were boiled before used.