Extended Data Fig. 5. Time-dependent production of MeTrp by wild-type KsTsrM and the Arg69Lys variant.
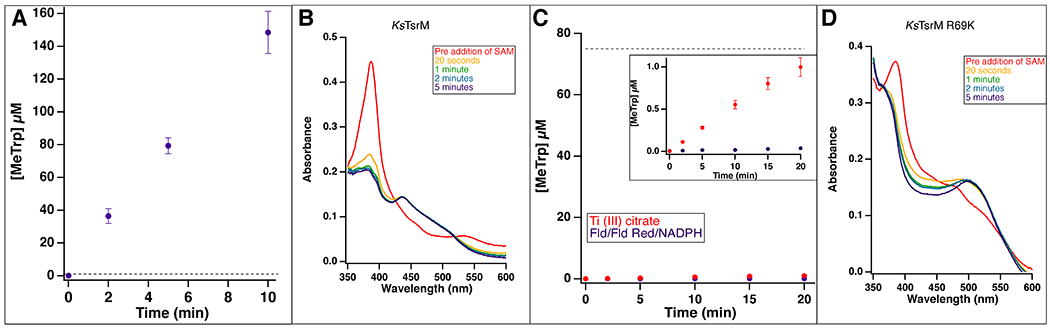
(A) Time-dependent production of MeTrp by KsTsrM (1 μM) using the flavodoxin/flavodoxin reductase/NADPH reducing system. kcat is 14 min−1. (B) UV-vis analysis of KsTsrM. KsTsrM was reduced with Ti (III) citrate to form cob(I)alamin. Upon addition of SAM to the reaction, the peak at 390 nm, indicative of cob(I)alamin, decays, while a peak at 520 nm, indicative of MeCbl, grows in. (C) Time-dependent production of MeTrp by the KsTsrM R69K variant using either Ti (III) citrate (red) or Fld/Fld Red/NADPH (purple) as reductant. Despite using 75 μM enzyme (indicated by dotted line), not even a full turnover is observed over 20 min by KsTsrM R69K with either reducing system. The inset displays a reduced Y-axis range to allow the small amount of activity in the presence of Ti (III) citrate to be observed. (D) UV-vis analysis of KsTsrM R69K. As in (B), KsTsrM R69K was reduced with Ti (III) citrate to generate cob(I)alamin. When SAM is added, cob(I)alamin decays and MeCbl grows in, indicating that MeCbl formation is not significantly diminished with this variant. Error bars represent the standard deviation of reactions conducted in triplicate, with the center point representing the average.
