Figure 1. Multiple Kingdom SpikeSeq (MK-SpikeSeq) enables robust quantitation of absolute abundances.
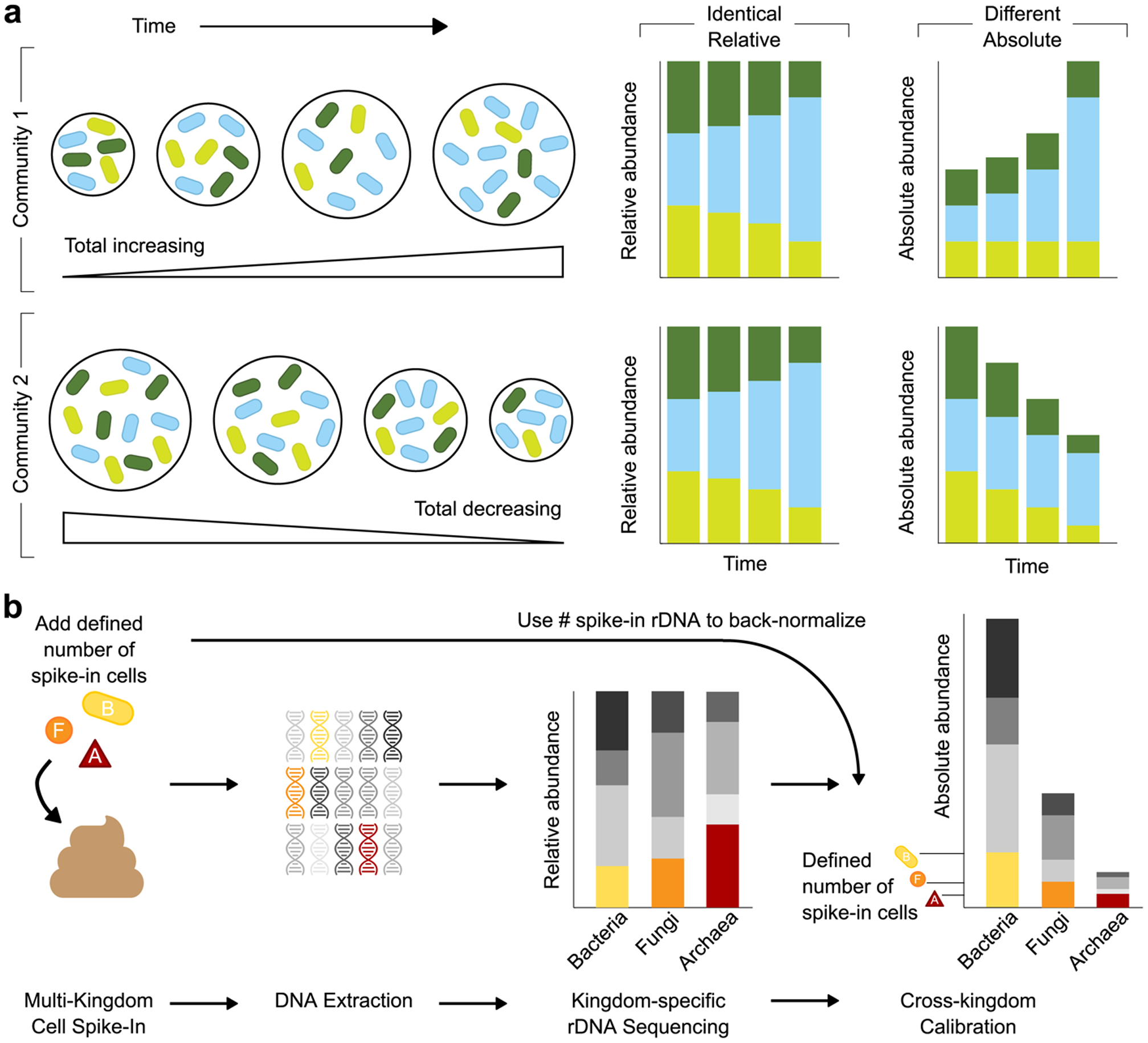
a, Schematic illustrating how relative abundance data can mask underlying community dynamics, rendering it challenging to distinguish different ecological scenarios. b, Overview of the MK-SpikeSeq pipeline. Prior to DNA extraction, defined amounts of each spike-in cell (bacteria (B), fungi (F) and archaea (A)) are added to each microbiome sample. Relative abundances of each microbial kingdom are then quantified using standard kingdom-specific rDNA amplicon sequencing. As the absolute abundances of each spike-in cell’s rDNA are known, these quantities can be used as back-normalization factors to calculate the absolute abundances of all other organisms present in each sample. The spike-in cells also serve as internal controls for the entire sample processing procedure, rendering the absolute quantification robust to factors such as sample-to-sample variability in DNA extraction efficiency.
