Extended Data Figure 5. MK-SpikeSeq identifies errors in sample processing of fungal communities.
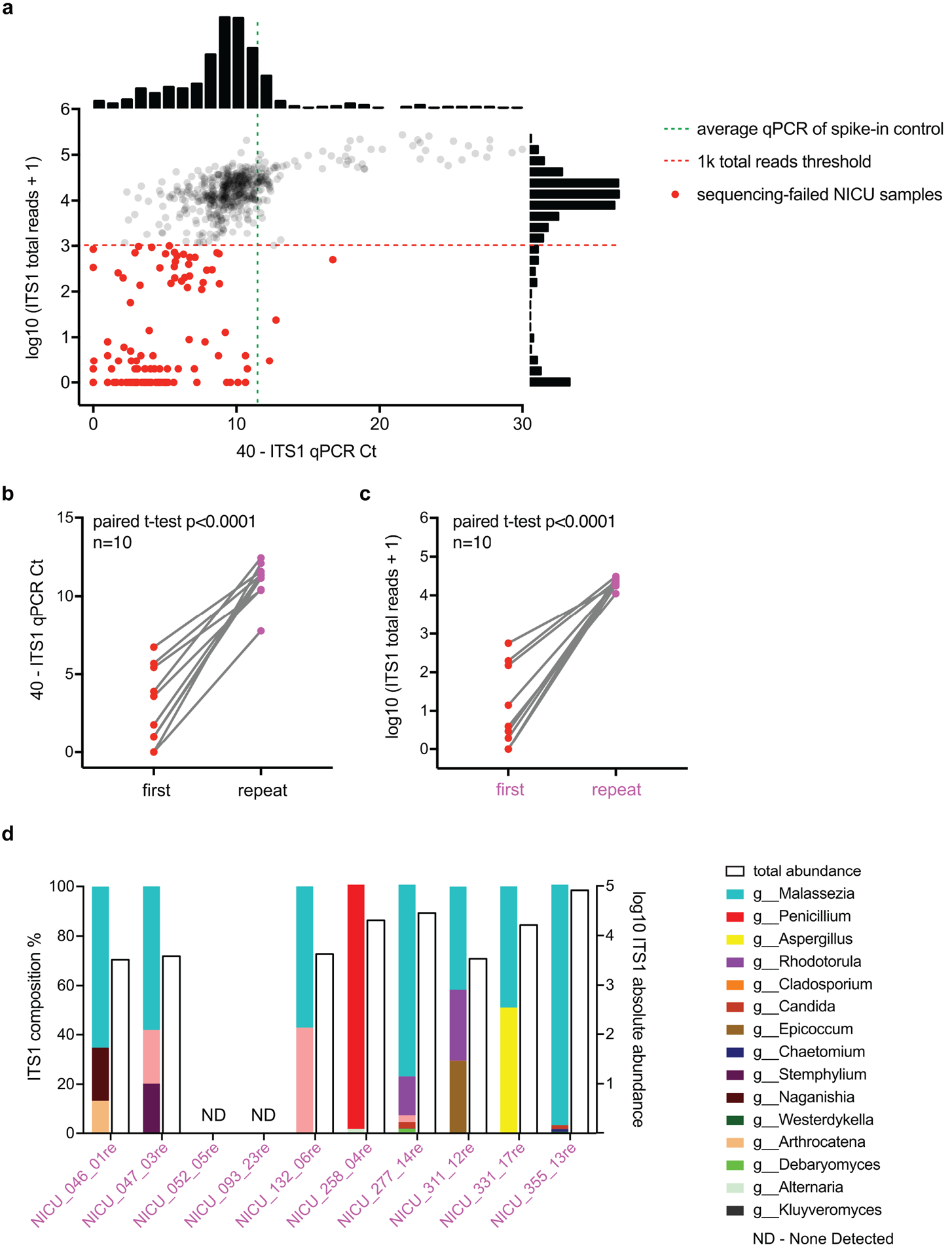
a, In our first phase of NICU sequencing (see Supplemental Text), we identified a number of samples, highlighted in red dots, that failed to yield >1k ITS1 reads per sample post quality filtering (red dashed line). Many of these sequencing-failed samples showed much lower (>5 deltaCt) ITS1 qPCR signals than the spike-in control (green dashed line), indicating poor DNA extractions of fungi in these samples. Shown next to the axes are frequency histograms of measurements. b, Reprocessing of 10 of these sequencing-failed samples led to increased ITS1 qPCR signals, indicating improved DNA extractions. c, These reprocessed samples also yielded desired >10k ITS1 reads, passing our rDNA sequencing criteria. For b/c, two-tailed paired student’s t test. d, Eight of the reprocessed samples showed non-zero fungal communities, and only two had no detectable fungal signal. Shown are the composition (colored bars) and total abundance (empty bars) of fungal communities in these reprocessed samples.
