Figure 1. Cyclin binding triggers a concerted conformational change in Cdk2.
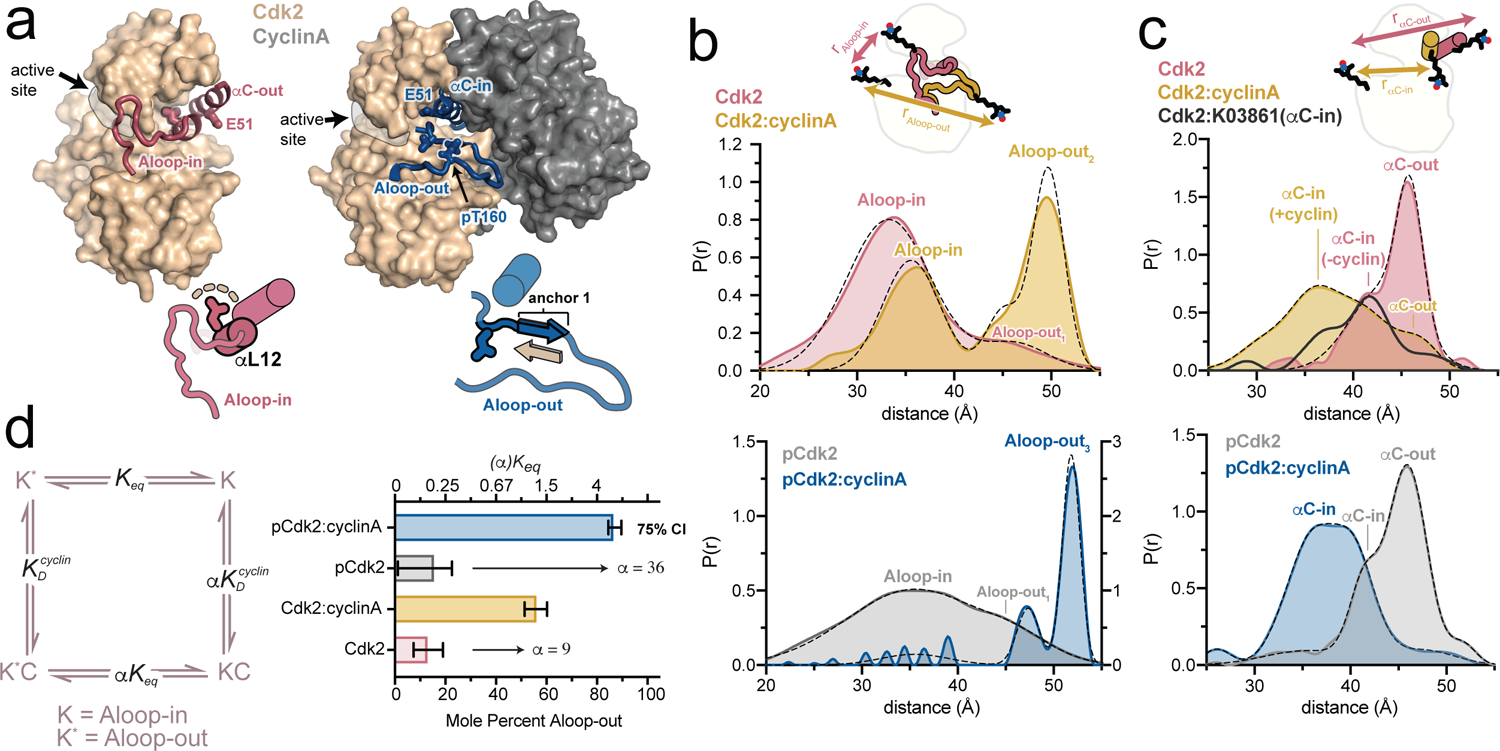
a) X-ray structures of Cdk2 in the Aloop-in/αC-out and Aloop-out/αC-in states (PDB IDs: 1HCK and 1JST), accompanied by schematics of the respective A-loop and αC-helix conformations. The segment of the A-loop highlighted in the schematics refolds from a helix (αL12) in the Aloop-in state to an anchoring β-strand in the Aloop-out state. b,c) DEER experiments tracking the A-loop (b) and αC-helix (c). Tikhonov-derived distance distributions are shown for monomeric Cdk2 and Cdk2:cyclinA dimer in the unphosphorylated state (top) and phosphorylated state (bottom). Dashed black lines represent Gaussian fits to the DEER data. Peak assignments are based on spin-spin distance calculations (see Supplementary Fig. 2 and Methods). The spin labeling schemes are represented schematically. Data for the αC-in inhibitor K03861 are shown in dark gray in c. Data for phosphorylated Cdk2 monomer are plotted on a different y-axis scale for clarity. d) Allosteric two-state model for cyclin binding to Cdk2, with K and K* representing the Aloop-in and Aloop-out states of the kinase, C representing the cyclin subunit, the Aloop-in/out equilibrium constant, and and representing microscopic equilibrium constants for cyclin binding to Aloop-out and Aloop-in states, respectively. The coupling parameter α describes the fold change in upon cyclin binding. The bar graph summarizes the values of and α derived from Gaussian fits of the DEER data. Error bars represent 75% confidence intervals, calculated from 50,000 simulations of Gaussian fits to the primary data.
