Figure 5. A divergent hub controlling allosteric coupling in Cdk2.
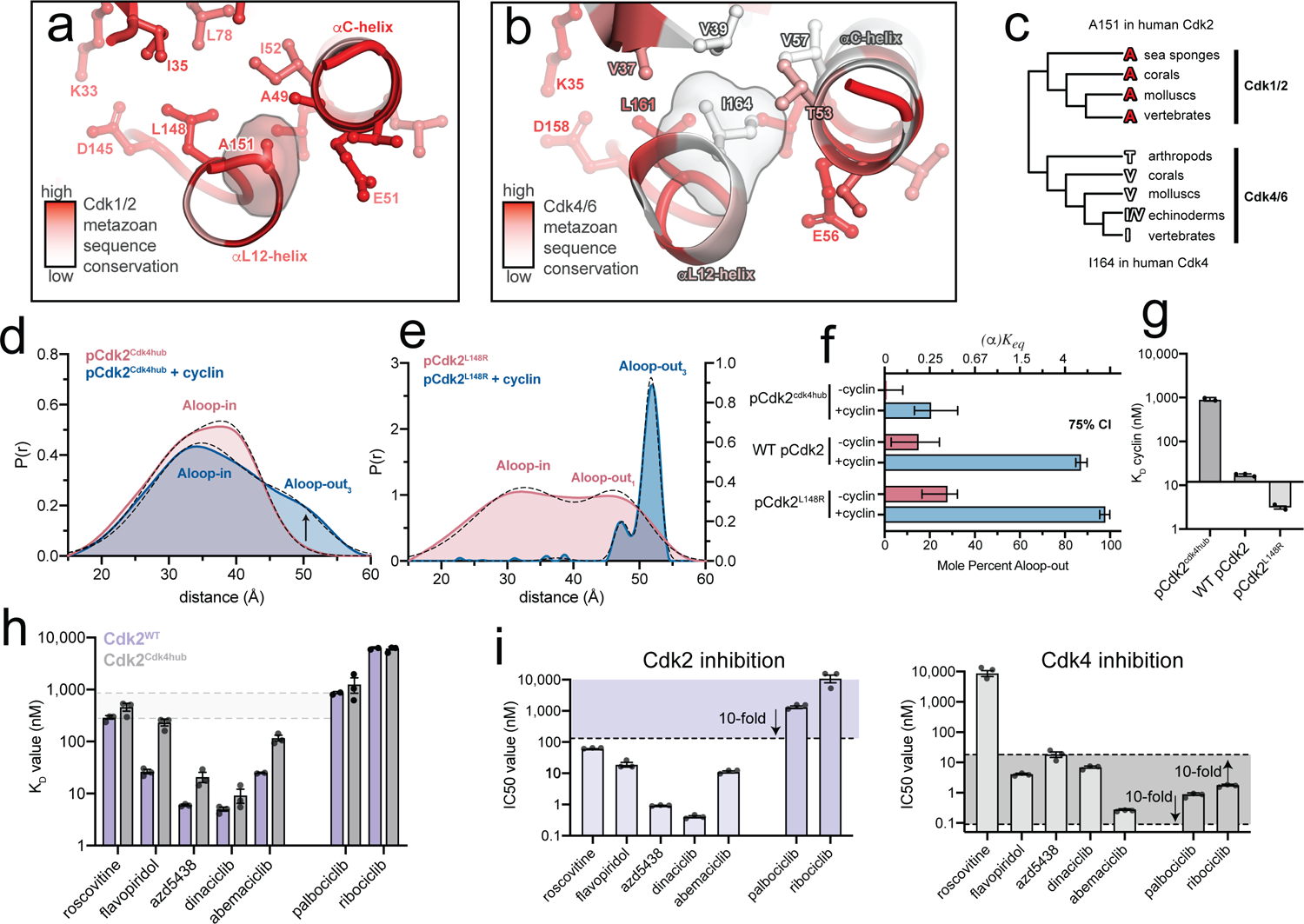
a,b) Metazoan sequence conservation in Cdk1/2 and Cdk4/6, determined from a set of 20 sequences (Supplementary Fig. 10), is mapped onto the structures of Cdk2 (left) and Cdk4 (right) in the Aloop-in conformation. Red represents strict conservation and white represents lower conservation. c) Divergence of the central hub residue (A151 in Cdk2, I164 in Cdk4) between Cdk1/2 and Cdk4/6 lineages. d) DEER data for the phosphorylated pCdk2cdk4hub mutant. Data for the unphosphorylated mutant are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. e) DEER data for the phosphorylated pCdk2L148R mutant. The monomer data are plotted on a different y-axis scale for clarity. Data for the unphosphorylated mutant are shown in Supplementary Fig. 12. f) Conformational equilibrium values for WT Cdk2, pCdk2L148R and pCdk2cdk4hub. Error bars represent 75% confidence intervals, calculated from 50,000 simulations of Gaussian fits to the primary data. g) Cyclin binding affinities measured by FRET for WT Cdk2, Cdk2L148R and Cdk2cdk4hub mutants. Values are mean ± S.E.M; n = 3 independent experiments. h) Inhibitor KD values measured by FRET for WT pCdk2:cyclinA and pCdk2cdk4hub:cyclinA. Values are mean ± S.E.M; n = 3 independent experiments. Data for the monomeric kinases are shown in Supplementary Fig. 13. i) IC50 values measured in kinase assays for the 7 inhibitors for pCdk2:cyclinA (left) and pCdk4:cyclinD (right). The shaded areas represent the range of IC50 values within 10-fold of the IC50 values for palbociclib and ribociclib. Values are mean ± S.E.M; n = 3 independent experiments.
