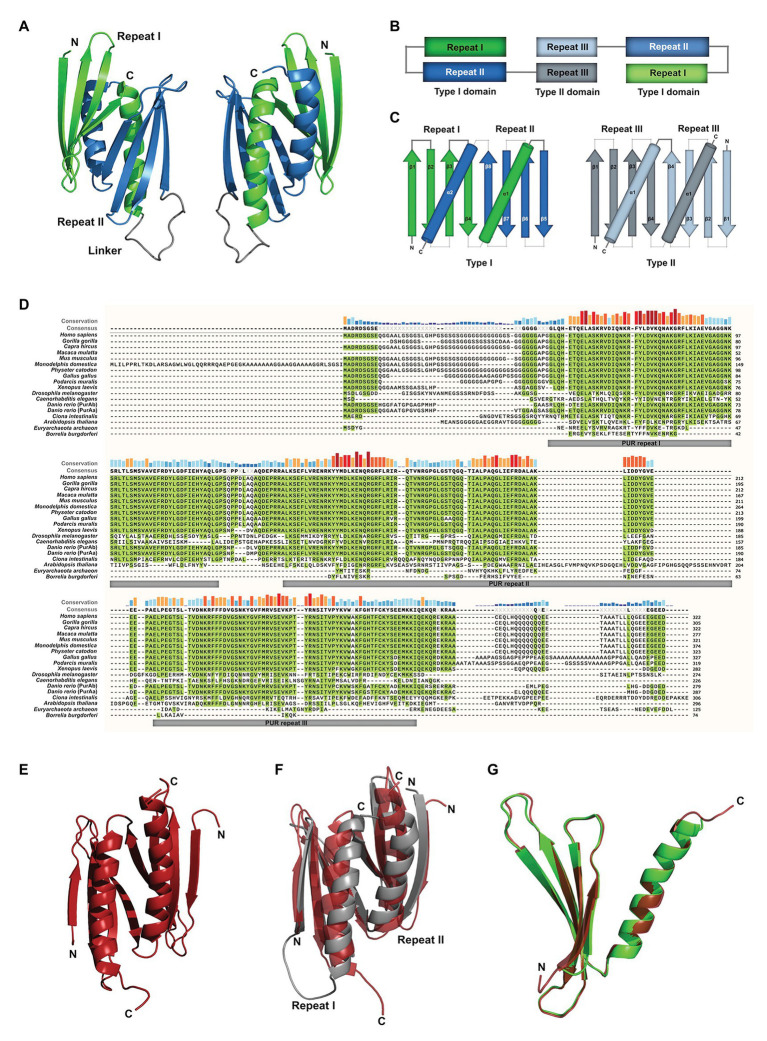
Figure 1.
Assessment of structural and sequence conservation between PURA proteins from different species. (A) Cartoon backbone model of the PURA DNA-binding domain of Drosophila melanogaster and a view rotated 180°. (B) Schematic illustration of the domain organization of the PURA homodimer. (C) Topology diagram of the type I and type II domain of PURA. (D) Amino acid sequence alignment of PURA from selected species with identical amino acids highlighted in green. The sequence similarity is notably higher within the PUR repeats and decreases with evolutionary distance. The alignment was executed using the MUSCLE algorithm and program MEGAX (Hall, 2013; Mello, 2018). (E) Cartoon backbone model of Borrelia burgdorferi PURA domain forming a type II homodimer (C). (F) Superposition of the DNA binding domain of D. melanogaster [shown in (A)] and B. burgdorferi [shown in (E); RMSD = 2.107]. (G) Superposition of D. melanogaster PURA repeat I and B. burgdorferi PURA (RMSD = 0.293).