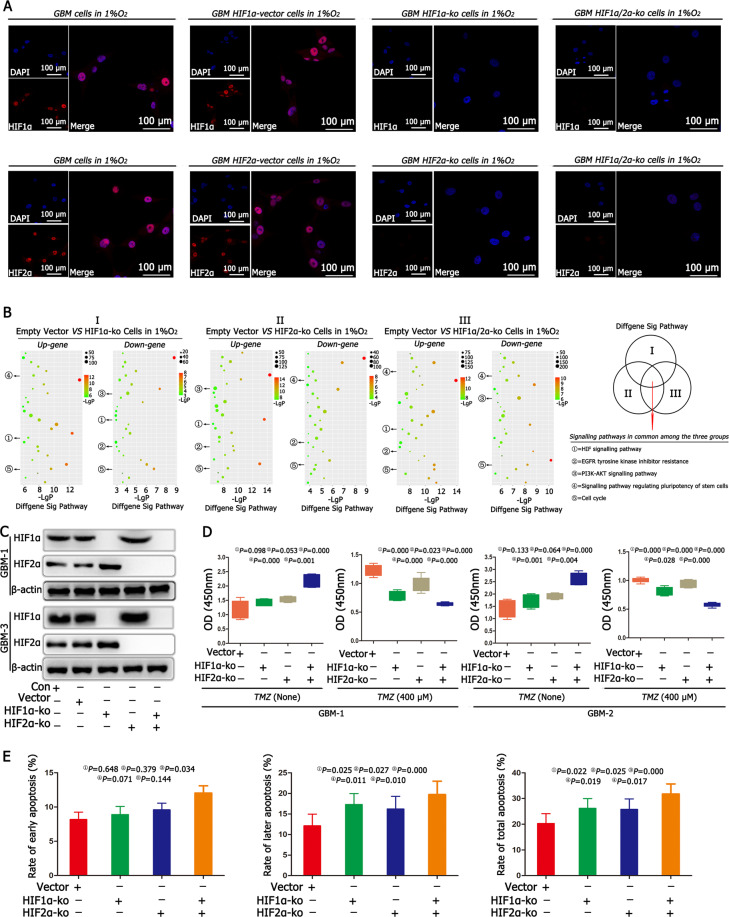
Fig. 2. HIF1α and HIF2α regulated cell proliferation and apoptosis.
A Immunofluorescence confirmed the successful knockout (KO) of HIF1α and HIF2α in HIF1α-KO, HIF2α-KO and HIF1α/HIF2α-KO cells. B We cultured empty vector cells, HIF1α-KO cells, HIF2α-KO cells, HIF1α/HIF2α-KO cells in 1% O2 for 24 h, KEGG pathway analysis revealed five common and significant signalling pathways, including the HIF signalling pathway, EGFR pathway, PI3K–AKT signalling pathway and signalling pathways regulating the pluripotency of stem cells and cell cycle using KEGG. C There were no differences in HIF1α and HIF2α between the control and empty vector groups after culturing both cells in 1% O2 for 72 h. However, the expression of HIF1α increased significantly after knocking out HIF2α; and HIF2α expression increased significantly after knocking out HIF1α. D After individually knocking out HIF1α or HIF2α, there were no differences in cell proliferation between the HIF1α-KO or HIF2α-KO cells and the empty vector cells. However, after simultaneously knocking out HIF1α and HIF2α, the cell proliferation rate increased significantly compared with the cell proliferation rates in other groups, including empty vector cells, HIF1α-KO cells or HIF2α-KO cells. Then, TMZ (400 μM) was added to the culture medium for another 72 h, and the cell proliferation became slower in HIF1α-KO or HIF2α-KO cells than in the empty vector cells; however, the slowest proliferation rate was found in the HIF1α/HIF2α-KO cells. E Cell apoptosis detection showed no difference in early apoptosis, but late and total apoptosis rates increased in HIF1α-KO or HIF2α-KO cells. However, after simultaneously knocking out HIF1α and HIF2α, there was a significant increase in early, late and total apoptosis rates compared with those in other groups. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA.