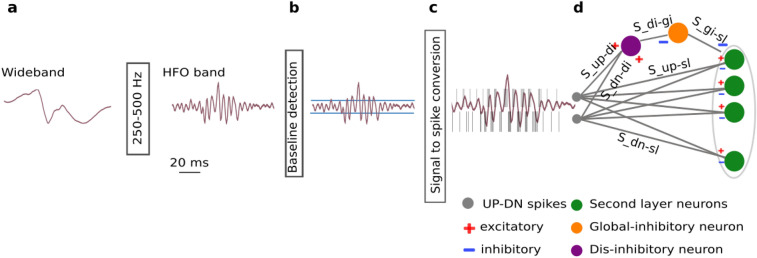
Figure 1.
HFO detection scheme. (a) The wideband ECoG is filtered in the HFO frequency band (250–500 Hz). (b) In the baseline detection stage, the background noise of the signal is used to set the signal-to-spike threshold. (c) The signal-to-spike conversion algorithm converts the analog signal into two streams of digital outputs: UP and DN spikes. (d) The SNN architecture for HFO detection and artifact rejection consists of input neurons (grey) receiving the input UP-DN spikes. These inputs project to a second layer of neurons (green) and to a dis-inhibitory neuron (purple). This neuron projects inhibitory synapses to a global-inhibitory neuron (orange), which is continuously inhibiting the second layer neurons. The synapses of the projections are excitatory (positive, red) or inhibitory (negative, blue).