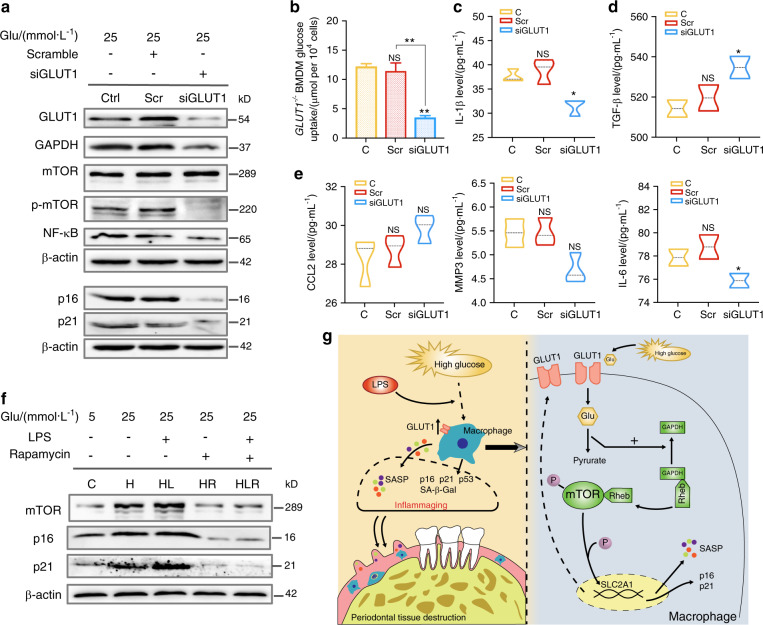
Fig. 5.
Induction of p16/p21 and SASP response by high glucose is relieved in GLUT1−/− macrophage. a GLUT1–mTOR pathway proteins expression in GLUT1-knockout BMDM. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting mouse GLUT1 was applied to build a GLUT1−/− BMDM model. The non-targeted siRNA as a negative control (Scramble). b Glucose uptake of GLUT1−/− BMDM. c–e The downstream SASP response in GLUT1−/− BMDM. The SASP response in GLUT1−/− BMDM was detected by ELISA, including early SASP (IL-1β), late SASP (CCL2, MMP3, and IL-6), and metabolic SASP (TGF-β). The concentration was expressed in pg·mL−1. f The mTOR downstream protein in BMDM treated with mTOR inhibitor, rapamycin, was detected by western blot. g Proposed model of mechanisms showed that macrophage inflammaging promotes periodontal damage by increasing the GLUT1 sensor response to high glucose and activating the mTOR pathway. C, BMDM cultured in low-glucose medium (5.5 mmol·L−1); H/HL, BMDM cultured in high-glucose medium (25 mmol·L−1) without or with LPS; H-R/HL-R, BMDM cultured in 12-h H/HL condition and then treated with 50 μg·L−1 rapamycin. *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. ***P < 0.001. NS, no significance. Repeated three times. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5)