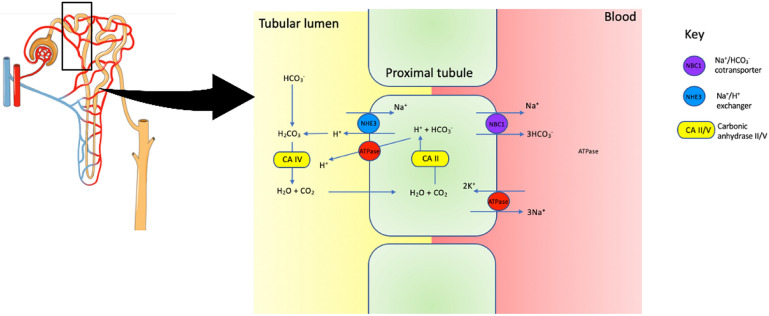
Fig. 2.
Proximal tubule. Intracellular carbonic acid (H2CO3−) dissociates into H+ and HCO3− under the action of carbonic anhydrase II (CAII). H+ secretion is facilitated by Na+/H+ exchanger, and Na+/HCO3− cotransporter is responsible for HCO3− transport. In the lumen, H+ reacts with HCO3− to form H2CO3, which dissociates into H2O and CO2 through the action of carbonic anhydrase V (CA V). Glucose, amino acids, phosphate and other substances are also reabsorbed through active and passive processes in the proximal tubule (mechanism not shown in schematic diagram). Damage in this region leads to Fanconi’s syndrome