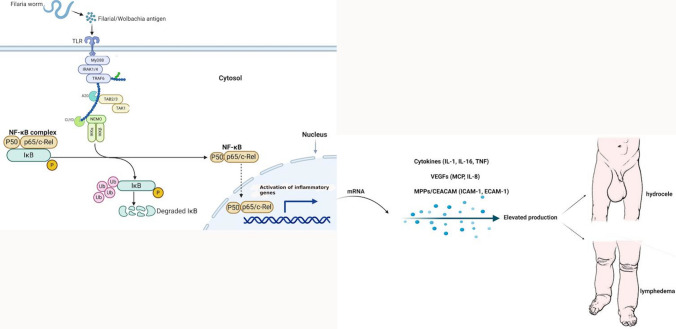
Fig. 2.
Role of NF-κB in lymphatic filariasis pathology. Toll-like signalling and cytokine receptors signalling by filaria antigens results in phosphorylation of IKK and activation of the IKK complex kinase activity. NF-κB is constitutively bound to IκB molecules which confine its localization to the cytosol. IKK starts phosphorylation of serine residues on IκB and promotes its polyubiquitination and degradation, thereby freeing NF-κB to enter the nucleus and activate transcription of target genes. Inflammation triggers expression of pro-inflammatory genes through IKK and NF-κB activation. Created with Biorender.com