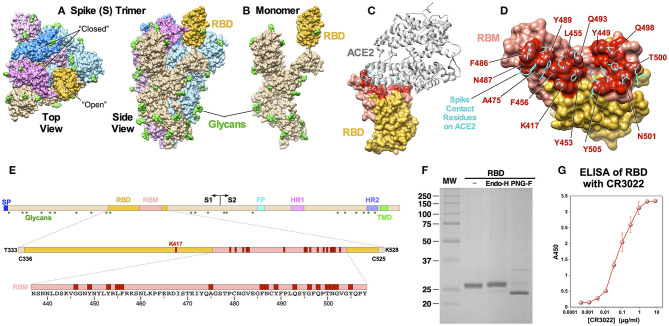
Figure 1.
Structural features of SARS-CoV-2 S protein and RBD immunogen. (A) A cryo-EM structure of a trimer (PDB: 6VSB). Top and side views are shown, and the “open” and “closed” conformational states of the RBD are indicated. Three monomers are shown in different colors with the RBD portions highlighted in darker shades. Glycans (N-acetylglucosamine) are shown in green. (B) A monomeric S protein in an “open” state. (C) A cocrystal structure of the RBD with ACE2 (PDB: 6M0J). The RBM is shown in pink and the ACE2 binding residues are highlighted in red. (D) Details of amino acid residues involved in ACE2 binding. Side chains on ACE2 that bind the RBD are shown in cyan. (E) Schematic diagrams of S protein, RBD and RBM showing major functional domains and features. The RBM is shown in pink and ACE2-contact residues are shown in red. Glycosylation sites are shown as green hexagon. (F) SDS-PAGE of purified RBD and after treatment with endoglycosidase H and PNGase F. (G) ELISA showing binding of the RBD to neutralizing mAb CR3022.