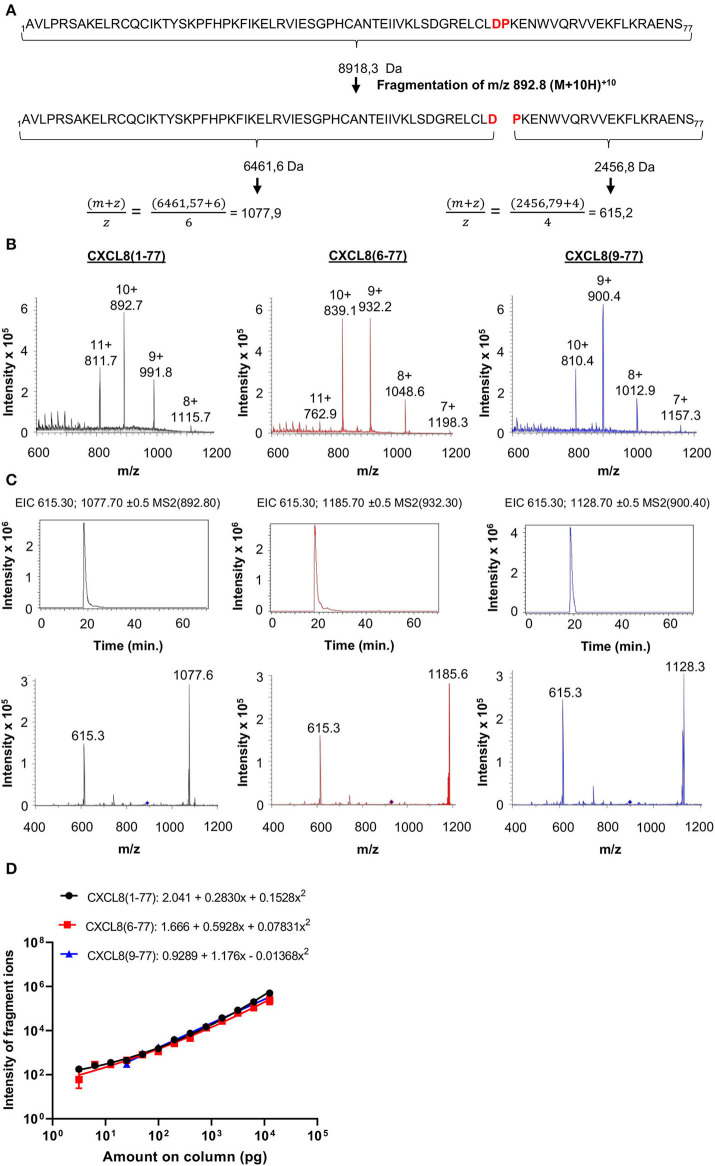
Figure 2.
Detection of CXCL8 proteoforms by top-down tandem mass spectrometry. (A) Parameters are optimized to ensure that only the acid-labile Asp-Pro (DP) bond breaks during low-energy fragmentation and only two fragment ions are generated. (B) Mass spectra (single MS) showing the intensity of multiple charged ions of CXCL8(1-77), CXCL8(6-77) and CXCL8(9-77) as a function of their m/z values. Ions with m/z values of 892.8 [for CXCL8(1-77)], 932.3 [for CXCL8(6-77)] or 900.4 [for CXCL8(9-77)] were isolated and fragmented with low energy CID. The resulting fragmentation spectra are shown in the lower panels in (C). Diamonds indicate the m/z value of the precursor ions selected for fragmentation. Extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) (top panels) show the detection of m/z values (±0.5) of the two signature fragment ions during protein elution. Relative quantification of CXCL8 forms is performed based on the intensity of the two major fragment ions in the EIC. (D) Dose-response curves for the simultaneous quantification of three CXCL8 forms in MRM mode (amounts ranging from 3.1 pg to 12.5 ng). Regression analysis was performed to fit curves to data. Results are represented as mean ± SEM (n ≥ 4).