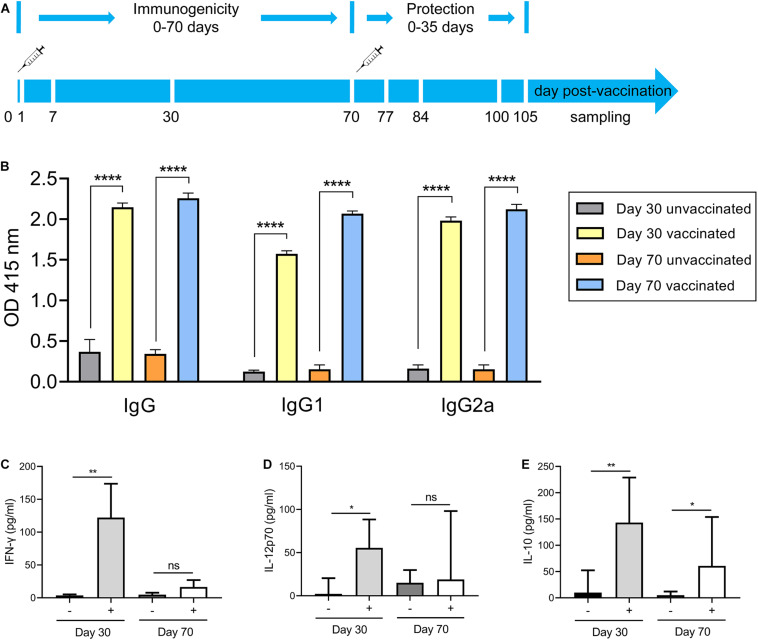
FIGURE 3.
Immunization scheme and study design. (A) Immunization scheme. The immune dose of 103 Δgra9 tachyzoites each mouse was injected into female BALB/c mice (n = 6 each group) by intraperitoneal injection and that day was designated as 0 day post-vaccination. The immunogenicity of Δgra9 vaccination was tested via the detection of specific anti-T. gondii IgG levels and cytokine productions in sera at 30 and 70 dpv. At 70 dpv, vaccinated or unvaccinated mice were secondly challenged by acute or chronic T. gondii infection to assess the protection. Within the vaccination and challenge period of total 105 days, the daily body weights, clinical signs, and survival rates of all mice were recorded in detail, and peritoneal fluid or serum samples were collected to evaluate immune response at the limited sampling periods as shown in (A). (B) The specific anti-T. gondii IgG and IgG subclasses (IgG1 and IgG2a) levels in vaccinated mice at 30 or 70 dpv. Unvaccinated naïve mice with the same ages were used as control (****P < 0.0001; Student’s t-test). (C–E) Cytokine productions in sera at 30 and 70 dpv. The levels of IFN-γ (C), IL-12p70 (D), or IL-10 (E) were determined by ELISA kits. –, unvaccinated mice; +, vaccinated mice (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant; Student’s t-test).