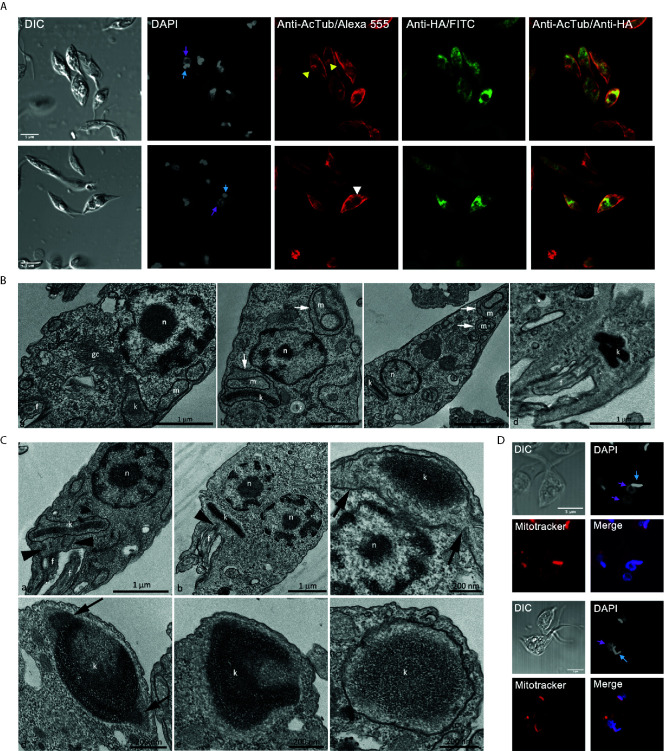
Figure 7.
Over-expression TcATAT-HA causes phenotypic alterations in acetylated α-tubulin distribution and on mitochondrion ultrastructure of epimastigotes. (A) Immunolocalization of ATAT-HA with rat monoclonal anti-HA antibodies and mouse monoclonal anti-acetylated α-tubulin (anti-AcTub) of Dm28c pTcINDEX-GW ATAT-HA epimastigotes induced with 0.5 μg/ml tetracycline for 24 h. Bar: 5 μm. DAPI was used as nucleus and kinetoplast marker. The light blue arrow indicates the kinetoplast and the pink arrow indicates the nucleus. Yellow arrowheads indicate accumulation of acetylated α-tubulin around the kinetoplast and the white arrowhead indicates accumulation of acetylated α-tubulin around the inclusion body-like structure. (B) Transmission Electron Microscopy of Dm28c pTcINDEX-GW ATAT-HA epimastigotes induced with 0.5 μg/ml tetracycline for 48 h. A general view showing the nucleus, mitochondrial branches, a small portion of the kinetoplast and the Golgi complex that was seen with its typical ultrastructure, without extended cisterns or space alteration between them (a). It was common to observe parasites presenting alterations in the mitochondrial branches and at the kinetoplast region, especially cristae swelling (b and c, white arrows). Parasites presenting a kinetoplast with multiple and electrodense networks were also observed (d). Cg – Golgi complex; f, flagellum; k, kinetoplast; m, mitochondrial branches; n, nucleus. Bar: 1 μm. (C) Transmission Electron Microscopy of Dm28c pTcINDEX-GW ATAT-HA. In uninduced epimastigotes the replicated kDNA is contained in a kinetoplast associated to two basal bodies (panel a, black arrowheads). Epimastigotes induced with 0.5 μg/ml tetracycline for 48 h presented atypical characteristics (b–f). In this case, the replicated kDNA is contained in a kinetoplast associated to a single basal body (b, black arrowhead), which result is kinetoplast division impairment in a cell with two nuclei. The kinetoplast region is continuous with mitochondrial branches (panel c, black arrows). The kDNA replication occurs during the S phase when the antipodal sites contain proteins involved in this process (d, black arrows). Since the kDNA replicates, but the kinetoplast does not divide, the network curves and folds over itself, becoming round and presenting an atypical topology. The kinetoplast shape also changes its format from disk to round (d-f). f, flagellum; k, kinetoplast; n, nucleus. Bars = 1 μm (a and b), 200 nm (c-f). (D) Dm28c pTcINDEX-GW ATAT-HA epimastigotes induced with 0.5 μg/ml tetracycline for 48 h and stained with Mitotracker CMTMRos. DAPI was used as nucleus and kinetoplast marker. The light blue arrow indicates the kinetoplast and the pink arrow indicates the nucleus. The upper panel shows a parasite with a kinetoplast containing a duplicated kDNA and two nuclei, while the lower panel shows a kinetoplast with an arched kDNA that did not suffer scission. Bar = 5 μm.