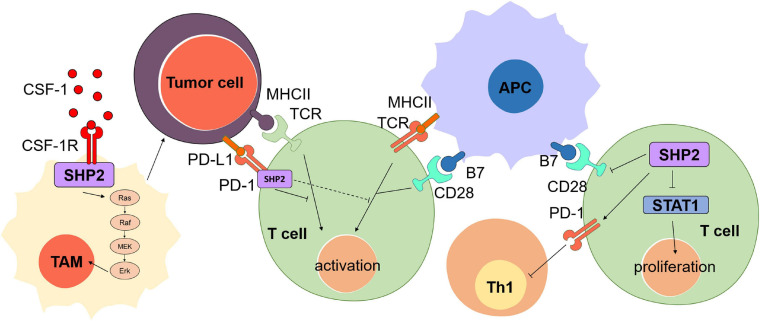
FIGURE 4.
The oncogenic role of SHP2 in tumor immune microenvironment. SHP2 binds to the T cell receptor (TCR) and prevents the activation of T cell induced by the signaling transduction among tumor cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and T cells. SHP2 binds to the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF-1R) under the stimulation of CSF-1 and then consequently activates Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk signaling and promotes the proliferation of tumor-associated macrophage (TAM), thus boosting the cancer cell survival. SHP2 in T cells inhibits the activation of T cell via blockage of the function of CD28 and STAT1.