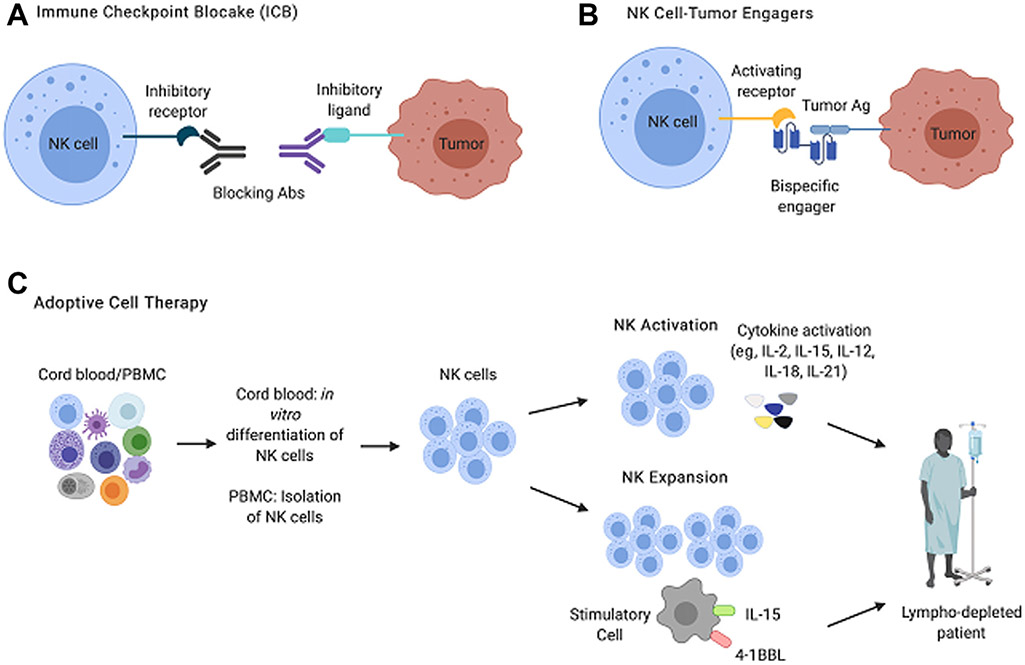
Fig. 3.
Major approaches to NK cell immunotherapy: 3 broad immunotherapeutic strategies to improve NK cell tumor surveillance currently used preclinically and in clinical trials. (A) ICB relies on the administration of monoclonal antibodies that prevent signaling through inhibitory receptors. (B) NK-tumor engagers are biologics with double or triple specificities. These molecules confer specificity to NK-tumor interactions by binding a protein antigen expressed by tumor cells and simultaneously delivering a stimulatory signal to the NK cell through an activating or cytokine receptor. (C) Adoptive cell therapy approaches infuse NK cells isolated from PBMCs, or differentiated in vitro from cord blood progenitors, into autologous, haploidentical, or allogeneic recipients. The transferred NK cells can be preactivated with cytokines to enhance NK cell effector functions or can be expanded using irradiated stimulatory cells engineered to express cytokines and stimulatory ligands. Ab, antibody.