Table 3.
Effect Sizes for Studies That Reported Effect Sizes Separately for Spanking and Physical Abuse
| Study | Outcome | Predictor | d | 95% Confidence interval | Beneficial outcomes | Detrimental outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|||||||
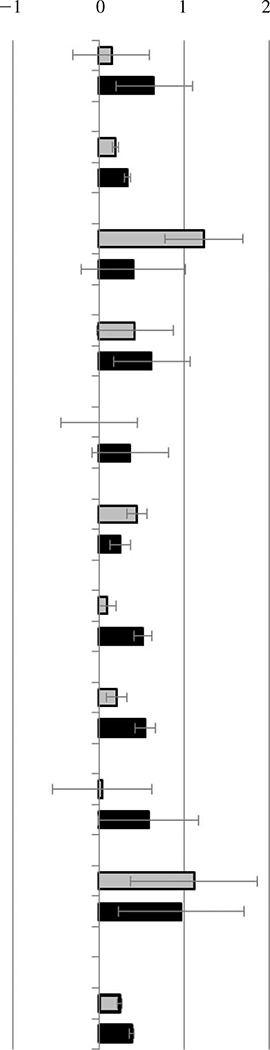
| Lau et al. (2003) | child externalizing behavior problems | spanking | .15 | −.30 | .60 | ||
| physical abuse | .65 | .19 | 1.10 | ||||
| Lau et al. (2005) | child externalizing behavior problems | spanking | .19 | .16 | .22 | ||
| physical abuse | .33 | .30 | .37 | ||||
| Bugental, Martorell, and Barraza (2003) | child mental health problems | spanking | 1.23 | .77 | 1.69 | ||
| physical abuse | .40 | −.21 | 1.01 | ||||
| Lau et al. (2003) | child mental health problems | spanking | .42 | −.03 | .87 | ||
| physical abuse | .62 | .17 | 1.07 | ||||
| Lau et al. (2003) | child low self-esteem | spanking | .00 | −.45 | .45 | ||
| physical abuse | .37 | −.08 | .82 | ||||
| Fergusson et al. (2008) | adult antisocial behavior | spanking | .45 | .33 | .57 | ||
| physical abuse | .25 | .13 | .37 | ||||
| Lynch et al. (2006) | adult antisocial behavior | spanking | .10 | .00 | .20 | ||
| physical abuse | .51 | .41 | .62 | ||||
| Fergusson et al. (2008) | adult mental health problems | spanking | .21 | .09 | .33 | ||
| physical abuse | .55 | .43 | .66 | ||||
| Miller-Perrin, Perrin, and Kocur (2009) | adult mental health problems | spanking | .04 | −.55 | .63 | ||
| physical abuse | .58 | −.01 | 1.17 | ||||
| Schweitzer, Zafar, Pavlicova, and Fallon (2011) | adult mental health problems | spanking | 1.12 | .38 | 1.86 | ||
| physical abuse | .96 | .23 | 1.70 | ||||
| Overall | spanking | .25 | .22 | .27 | |||
| physical abuse | .38 | .29 | .41 | ||||
