Figure 6: BLA-plPFC-specific CB1 deletion phenocopies stress-induced synaptic strengthening and exacerbates stress-induced anxiety.
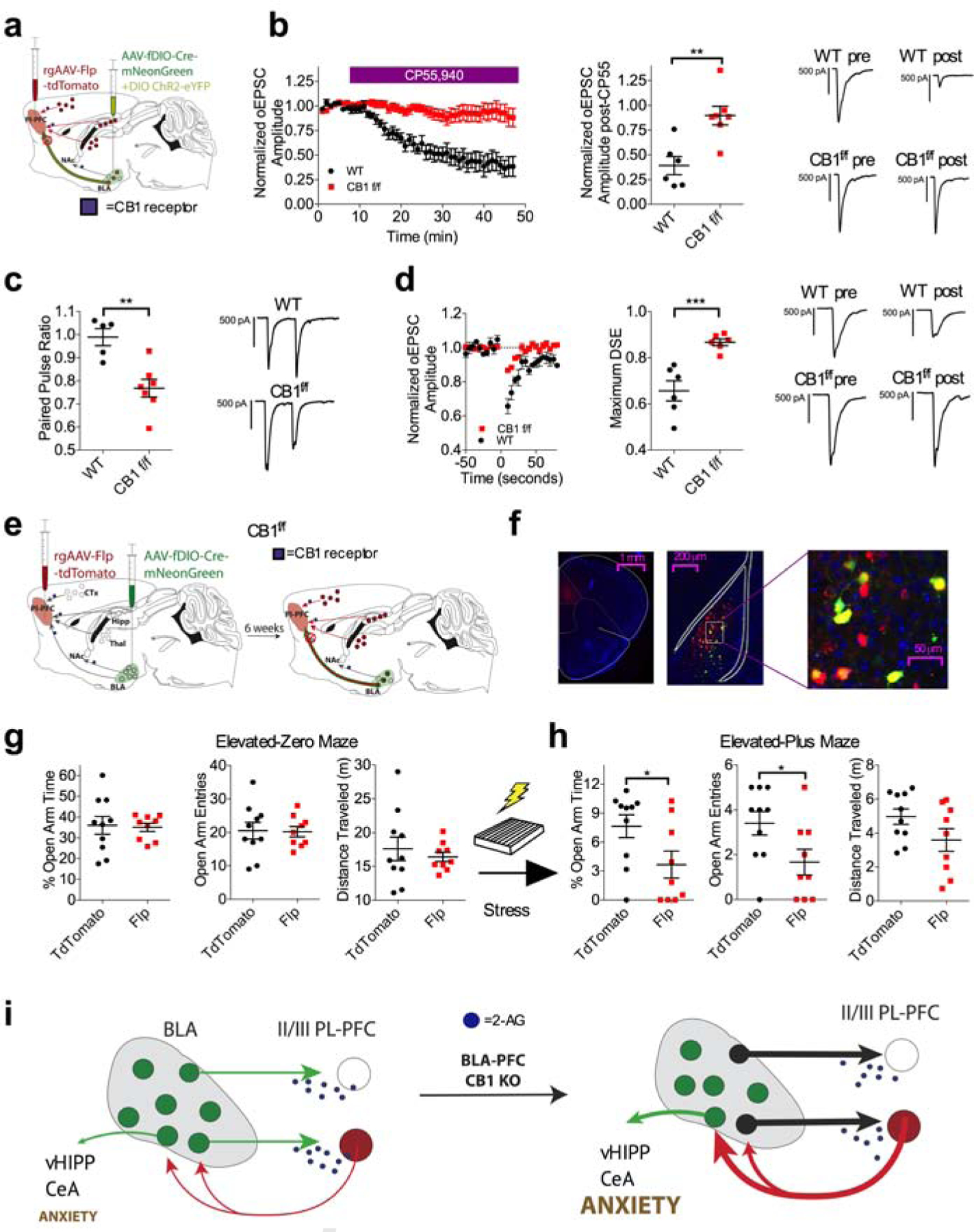
(a) Schematic for physiological validation of the INTRSECT approach for deletion of the CB1 receptor from plPFC projecting BLA neurons.
(b) Effect of 5 μM CP55,940 on oEPSC amplitude at BLA-L2/3 plPFC synapses. CP55,940-induced depression of oEPSC amplitude is dramatically attenuated in CB1f/f INTRSECT mice (n=7, N=3) compared to WT control INRSECT mice (n=6, N=2; p=0.0028).
(c) Effect of BLA-plPFC CB1 deletion on PPR at BLA-L2/3 plPFC synapses (WT: n=5, N=2; CB1f/f: n=7, N=3; p=0.0026).
(d) Effect of BLA-plPFC CB1 deletion on DSE at BLA-L2/3 plPFC synapses (WT: n=6, N=2; CB1f/f: n=6, N=3; p=0.0010).
(e) Schematic of INTRSECT approach for deletion of the CB1 receptor from plPFC projecting BLA neurons for behavioral characterization.
(f) Representative images showing injection site of rAAV2-EF1-Flp-tdTomato in the plPFC and AAV5-fDIO-Cre-mNeonGreen in the BLA, showing co-expression of rAAV+ neurons (red) and Cre+ neurons (green) in the BLA.
(g) Effect of BLA-plPFC CB1 deletion on anxiety-like behavior in the EZM in stress-naive mice. There were no significant differences in anxiety-like behavior in Flp injected CB1f/f mice (N=9) compared to Td-tomato injected CB1f/f mice (N=10).
(h) Effect of BLA-plPFC CB1 deletion on anxiety-like behavior in the EPM following stress exposure. Flp injected CB1f/f mice (N=9) show significantly decreased % open-arm time (p=0.0421) and decreased open-arm entries (p=0.0391), without changes in total distance travelled (p=0.1020) compared to control virus-injected littermates (N=10).
(i) Deletion of CB1 from BLA projections to the plPFC induces a stress-like synaptic phenotype and exacerbates the anxiogenic effects of stress exposure.
All error bars represent ± SEM. “n” represents number of neurons, “N” represents number of mice. P values reported from two-tailed unpaired t-test (b,c,d,g,h).
